* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drugs anti
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
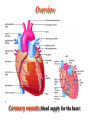
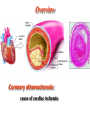
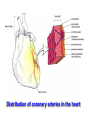
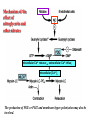
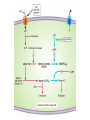
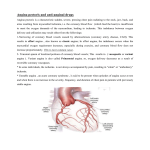
抗心绞痛药 Antianginal Drugs Overview • • – – – What’s Angina pectoris Cause and the classification of angina pectoris : Atheromatous obstruction of the large coronary vessels (atherosclerotic angina, classic angina); 劳累性心绞痛:稳定型,初发型,恶化型 Transient spasm of localized portions of the large coronary vessels (angiospastic or variant angina); 自发性心绞痛:卧位型,变异型,急性冠脉功能不全,梗死后心绞痛 Both causes 混合性心绞痛 Unstable angina pectoris: initial onset type; accelerated type; spontaneous type associated with atheroscleosis plaque and thrombus formation may lead to myocardial infarction Overview Coronary vessels: blood supply for the heart Overview Coronary atherosclerosis: cause of cardiac ischemia Distribution of coronary arteries in the heart Overview oxygen requirement oxygen supply imbalance • Primary cause of angina pectoris: – In classic angina, the imbalance occurs when the myocardial oxygen requirement increases; “angina of effort” – In variant angina, oxygen delivery decreases as a result of reversible coronary vasospasm. “vasospastic or Prinzmetal's angina” afterload preload Overview Myocardial oxygen demand is diminished by: • • • • Reducing contractility Reducing heart rate Reducing the preload Reducing the afterload Wall tension Myocardial oxygen supply is increased by: • • Dilating conduct coronary arteries ( coronary blood flow) Promoting regional distribution ( in ischemic regions) Treatments: • Non-drug treatment:经皮冠状动脉成形术(percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, PTCA), 冠脉搭桥术 ( coronary artery bypass graft surgery, CABG ) • Drug treatment Antianginal Drugs Effects of antianginal drugs: • Reducing oxygen demands • Increasing oxygen supply • Others: Anti- platelet coagulation and thrombus formation Antianginal drugs: • • • • • • Organic nitrates receptor blockers Calcium channel blockers Anti-platelet agents ACEIs Fish oil Nitrates & Nitrites nitroglycerin • Quick tolerance and cross-tolerance; • Pharmacokinetic factors determine the selection; Nitrates & Nitrites - Pharmacokinetics • Low oral bioavailability (eg, nitroglycerin and isosorbide dinitrate, typically < 10–20%). • Sublingual is normally used. Transdermal and buccal absorption from slow release preparations. • Amyl(戊基) nitrite and related nitrites can be used with inhalation route. • Duration of effect is very brief (Unchanged nitrate t1/2=2-8 minutes, partially denitrated metabolites longer t1/2= 3 hrs). So micro-pump is very common in hospital usage. Nitrates: Nitroglycerin (硝酸甘油) - Pharmacological actions • Dilating vessels and reducing heart loads wall tension ; reflex tachycardia • Redistribution of coronary circulation dilating conduct artery: collateral circulation reducing wall tension: blood flow in ischemic subendocardial area • Alleviating ischemic injury • Anti- platelet coagulation Nitrates: Nitroglycerin (硝酸甘油) Influence of organic nitrates and dipyridamole on the blood supply of ischemic area Mechanism of the effect of nitroglycerin and other nitrates Intracellular Ca2+ release↓,extracellular Ca2+ influx↓ Intracellular [Ca2+] ↓ The production of PGE or PGI2 and membrane hyper-polarization may also be involved. Nitrates: Nitroglycerin (硝酸甘油) - Clinical uses • Angina pectoris: all kinds, especially stable type • Heart failure - Adverse reactions • Symptoms due to vasodilation: headache, postural hypotension, etc. • Increase in heart rate and contractility • Others: methaemoglobinaemia(高铁血红蛋白) • Tolerance : avoiding steady-state plasma concentration; supplement of agents containing –SH (captopril, NAC), VitC Nitrates Other nitrates Isosorbide dinitrate (硝酸异山梨酯) Isosorbide-5-mononirate (5-硝酸异山梨酯) Compared with nitroglycerin: • • • Similar but weaker effect Acting slowly but lasting longer Larger individual variation and more adverse effects receptor blockers - Pharmacological action • Reducing oxygen demand: heart rate and contractility • Increasing oxygen supply: diastolic period : perfusion time vascular tone in normal regions : blood flow in ischemic regions • Others: Improving myocardial metabolism Increase oxygen supply Inhibiting coagulation of platelets receptor blockers - Clinical uses stable and unstable pectoris, especially associated with hypertension or arrhythmias, even with myocardial infarction; but not used for variant angina pectoris - Notes • • • • • Dose individualization: starting from small dose Withdraw gradually and slowly: symptom rebound Cardiac depression Inducing asthma Combination with nitroglycerin Calcium channel blockers - Pharmacological actions • Reducing myocardial oxygen remand: heart loads : nifedipine heart rate and contractility : verapamil and diltiazem • Increasing myocardial blood supply • Inhibiting coagulation of platelets • Protecting ischemic myocardial cells - Clinical uses stable and variant type: nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem unstable type: verapamil, diltiazem Calcium channel blockers - Toxicity • Cardiac depression, including cardiac arrest, bradycardia, atrioventricular block, and heart failure. • Relatively short-acting calcium channel blockers have the potential to enhance the risk of adverse cardiac events. • Slow-release and long-acting vasoselective calcium channel blockers are usually well tolerated. Patients receiving -adrenoceptor-blocking drugs are more sensitive to the cardiodepressant effects of calcium channel blockers. • • Tolerable toxicity: flushing, dizziness, nausea, constipation, and peripheral edema. Other drugs Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) Nicorandi (尼可地尔) • a potassium channel opener Molsidomine (吗多明) • Producing NO → stimulate guanylyl cyclase (GC) →increase cGMP → relaxes vascular smooth muscle Dipyridamole (双嘧达莫,潘生丁) • Inhibiting adenosine uptake and cAMP degradation • Inhibiting pletelet aggregation Summary of antianginal drugs nitroglycerin Heart rate Contractility Wall tension Oxygen demand Blood pressure blockers Ca2+ antagonists combination* / / / : increase, : markedly increase; : decrease, : markedly decrease; : variable according to the dose and effect of each drug ; * blockers combined with nitroglycerin or Ca2+ antagonists (nifedipine; combination with verapamil/diltiazem not be recommendated) Caution: Combination may potentiate the antianginal effects, but may induce severe hypotension Thanks!