* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benzene and Aromatics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
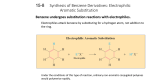
Benzene The aromatics Benzene Benzene and its derivatives are part of a special group called aromatics. When it is a substituent group it is called a phenol group. Benzene Benzene, is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. It is sometimes abbreviated Ph–H. Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell and a relatively high melting point. Because it is a known carcinogen, its use as an additive in gasoline is now limited, but it is an important industrial solvent and precursor in the production of drugs, plastics, synthetic rubber, and dyes. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil, and may be synthesized from other compounds present in petroleum. Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon Toluene also known as methylbenzene, is a clear water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is an aromatic hydrocarbon that is widely used as a solvent. Like other solvents, toluene is also used as an inhalant drug for its intoxicating properties; however this causes severe neurological harm. Phenol is a toxic, white with a slightly pink tinge, crystalline solid. Its chemical formula is C6H5OH and its structure is that of a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to a phenyl ring, making it an aromatic compound. Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H7N. It is the simplest and one of the most important aromatic amines, being used as a precursor to more complex chemicals. Its main application is in the manufacture of polyurethane. Styrene also known as vinyl benzene as well as many other names (see table), is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This aromatic hydrocarbon is a colorless oily liquid that evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concentrations confer a less pleasant odor. Styrene is the precursor to polystyrene and several copolymers. Naphthalene is a crystalline, aromatic, white, solid hydrocarbon with formula C10H8 and the structure of two fused benzene rings. It is best known as the traditional, primary ingredient of mothballs. It is volatile, forming an inflammable vapor, and readily sublimes at room temperature, producing a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass.[1]