* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download najważniejsze izoenzymy cytochromu p450 biorace udział w
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
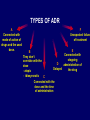
Jarosław Woroń PharmD, PhD MISTAKE IN PEDIATRIC PHARMACOTHERAPY Chair Of Pharmacology, Dept. Of Clinical Pharmacology Jagiellonian University College of Medicine Krakow ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS Are one of the first ten causes of death 20% of funds spent on health protection is used for ADR 10-15% of hospitalization is connected with ADR 5-9% of hospitalization costs are costs of ADR 30-60% of cases of ADR can be prevented TYPES OF ADR A Connected with mode of action of drugs and the used dose. F Unexpected failure of treatment E B Connected with They don’t stopping correlate with the D administration of dose Delayed the drug - atopic - idiosyncratic C Connected with the dose and the time of administration FACTORS INCREASING THE RISK OF MAKING A MISTAKE IN PHARMACOTHERAPY 1. polypharmacy 2. Patients treatment by a few doctors who don’t consult the given pharmacotherapy w 3. Lack of accepted standards in pharmacotherapy 4. Lack of pharmacotherapy control- the posibility of repeating mistakes 5. Self- medication SOURCES OF MEDICAL MISTAKES IN PHARMACOTHERAPY • - attractive pharmacotherapy- for the patients is the one which brings fast results and can put the patients in danger of side effects • - the rule of three- wrong drug in the wrong dose for the wrong patient • - the pharmacotherapy without considering the limits and contraindications, before starting the treatment carelessly intervied patient • - treating the child as a miniature of an adult- a lot of ADR depend on the age of the patient DIFFERENCES IN PHARMACOKINETIC PARAMETERS IN PEDIATRICS • - small area of gastrointestinal tract • - lower production of acid, pepsynogen and slower emptying of the stomach, irregular peristalsis, lower production on pancreas enzymes and bile • - immaturity of intestinal enzymesCYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein • - it’ s best to give to children drugs in the form of syrupes and solutions DISTRIBUTION • - in distribution we observe increased volume of distribution in the water phaseit’s better to calculate the doses depending on the area of the body, weaker connection of drugs with albumins, increased permeability of blood/brain barrier- increased risk of ADR METABOLISM Unsatisfactory ability of cytochrome P450 isoenzymes, which take partin drug metabolism, weaker connection with glucuronic acid ELIMINATION • - kidney activity in newborn babies constitutes 30-40% of activity in comparison with adult OFF-LABEL DRUG USE • - every disease has its own characteristics • - lack of possibility of observationof drug safety profile • - lack of information about ADR • - lack of possibility of determiningthe ratio between the benefit and the risk CONTRAINDICATION OF DRUG USE DEPENDENT ON AGE • • • • • • • Can be used above -Thiocodin -12 years of age - Sulfarinol -12 years of age - Dextrometorphan- 6 years of age - Detreomycin maść- 11 years of age - Acetylosalicylic acid- 12 years of age - Actifed , Actitrin- 6 years of age USE OF PROMETAZINE IN CHILDRENDOUBTED BENEFIT AND HIGH RISK Absolutly contraindicated undre 2 years of age- can cause breath depresion and it can result in sudden newborn death syndrome drowsiness dizziness Weakening of the muscles Poor slightniewyraźne widzenie Combined with metamizole increases the risk of hypothermia DRUG INTERACTIONS • - pharmacokinetic • - pharmacodynamic • - common profile of side effects HOW TO PREVENT ADR IN CHILDREN • - use of the drugs according to registration • - avoidance of unwanted drug interactions • - monitoring of ADR • - it must be remembered a child is not a miniature of an adult