* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download types of studies in diabetes epidemiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
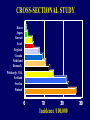
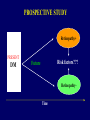
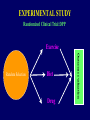
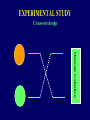
TYPES OF STUDIES IN DIABETES EPIDEMIOLOGY Nam-Ham Cho, Ajou University TYPES OF STUDIES BASED ON: • Purpose • Time • Cost • Feasibility TYPES OF STUDY Observational Descriptive Analytical – Cross-sectional – Retrospective – Prospective Experimental – Clinical Trial – Community Intervention Trial – Field Trial A STUDY DESIGN FOR THE OUTCOMES OF DIABETES • Diabetes • Morbidity (Complications) • Mortality (Death) • Economics • Treatment • Education • Prevention & Control • Intervention TIME AND TYPES OF STUDY PAST PRESENT Retrospective Cross-sectional Time FUTURE Prospective CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY PRESENT Cross-sectional Time ANALYTICAL STUDY A cross-sectional study: – Privides a snap shot – Is simple – Provides associated factor – Is first line of epidemiologic research CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY What is different about: • DM • Morbidity (Complications) • Mortality (Death) How is it different about: • SES • Age at onset • Season CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY Korea Japan Kuwait Israel England Canada Netheland Denmark Pittsburgh, USA Scotland Sweden Finland 0 10 20 Incidence /100,000 30 RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Determining differences in: • • • • • • Life style Diet Reproductive on Medication Family Hx Genetics PRESENT PAST Time Disease RETROSPECTIVE STUDY: PROS & CONS PRO • • • • • • Suitable for rare diseases Inexpensive Minimal ethical problems Short study time Small # of subjects Subjects need not volunteer CON • • • • • Susceptable to selection & memory bias Inconsistency: definitions of symptoms or diseases may have been modified over time. Can not determine incidence Limitations in data Relative risk approximation PROSPECTIVE STUDY Retinopathy+ PRESENT DM Risk factors??? Future Retinopathy- Time PROSPECTIVE STUDY: PROS & CONS PRO • • • • Less variability to bias No recall necessary Incidence determined Relative risk accurate CON • • • • • • • • • Consistent disease definitions & symptoms. Longer time Common disease only Expensive Ethical concern A high drop-out rate Volunteers needed A large # of subjects needed The Hawthorne-effect TYPES OF STUDIES AND GOALS CROSS-SECTIONAL Understand RETROSPECTIVE Estimate risk factors PROSPECTVE Validate risk factors Prevention-Control-Intervention-Education-Management EXPERIMENTAL STUDY • Animal • Drug trials • Human EXPERIMENTAL STUDY Randomized Clinical Trial:DPP Exercise Diet Drug Outcome evaluation Random Selection EXPERIMENTAL STUDY Cross-over design Outcome evaluation Review Questions (Developed by the Supercourse team) • What are the advantages and disadvantages for retrospective studies? •What are the advantages and disadvantages for prospective studies?