* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biologically Based Systems
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
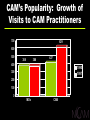
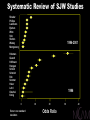
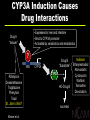
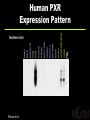
What Is CAM? … medical and health care practices outside the realm of conventional medicine, which are yet to be validated using scientific methods Complementary: together with conventional practices Alternative: in place of conventional practices CAM Domains Biologically Based Systems Diets Herbals Energy Therapies Reiki Magnets Qi qong Massage Chiropractic Common CAM Practices Manipulative and Body-Based Systems Yoga Prayer Meditation Homeopathy Naturopathy Alternative Medical Systems Mind-Body Medicine CAM’s Popularity: Growth of Visits to CAM Practitioners 700 629 600 500 386 388 427 400 1990 1997 300 200 100 0 MDs CAM Conventional Medicine “Push” Factors Failure to yield cures Adverse effects of orthodox regimens Lack of practitioner time Dissatisfaction with the technical approach Fragmentation of care by specialists CAM Therapies “Pull” Factors Media reports of dramatic results Belief that CAM treatments are natural Patient empowerment Focus on spiritual and emotional well-being Therapist providing “touch, talk, time” CAM: The Evidence Efficacy Abundant anecdotes and tradition Small studies Safety Displacing/interfering with proven therapies Inherent toxicity of CAM products NCCAM’s Mission Conduct rigorous research on CAM practices Educate and train CAM researchers Inform consumers and health professionals Setting Priorities for NIH Research Burden of disease Use by U.S. public Opportunity to reveal new principles Data from preliminary studies encouraging Studies are ethical, feasible Private investment in research is low, lacking Investment Priorities Extramural Program Phase I-III studies of many CAM approaches Pre-clinical and translational research Research training Intramural Program Clinical and translational studies of CAM approaches to age-related stressors Research training NCCAM Research Support FY 2001 Clinical Basic Status of Phase III Randomized Controlled Trials St. John’s Wort for major depression In press Shark cartilage for lung cancer In progress Ginkgo biloba to prevent dementia In progress Acupuncture for osteoarthritis pain In progress Status of Phase III Randomized Controlled Trials Glucosamine/chondroitin for osteoarthritis In progress Vitamin E/selenium for prostate cancer In progress EDTA chelation therapy for CAD Award pending Saw palmetto/P. africanum for BPH Announced CAM Domains Biologically Based Systems Diets Herbals Energy Therapies Reiki Magnets Qi qong Massage Chiropractic Common CAM Practices Manipulative and Body-Based Systems Yoga Prayer Meditation Homeopathy Naturopathy Alternative Medical Systems Mind-Body Medicine St. John’s Wort Medicinal herb Widely used $6 billion European sales (1998) $140 million U.S. sales (1998) Complex mixture of > 2 dozen compounds Antidepressant constituent = hyperforin Drug interactions oral contraceptives indinavir cyclosporin Systematic Review of SJW Studies Shrader Phillips Laakmann Bjerken Witte Volz Shelton Wiedey Montgomery 1996-2001 Holoman Quandt Hoffmann Hansgen Schilch Schmidt Reh Sommer Huber Lehrl Osterhei Konig 1996 0 Bars = one standard deviation 10 20 Odds Ratio 30 40 NIH Multicenter Trial of SJW in Major Depression 8-week acute efficacy phase 18-week maintenance phase Active drug and placebo control arms Study Outcome Primary Endpoints Change in HAM-D score Rate of complete response (CGI-I 2 and HAM-D 8) It’s All “Natural”…! “People can be induced to swallow anything, provided it is sufficiently seasoned with praise.” Jean Moliere St. John’s Wort Lowers Blood Levels of HIV Protease Inhibitor Indinavir Indinavir level (ug/ml) 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 HIV Inhibition threshold 0.1 0 Indinavir alone Piscitelli et al. Indinavir+SJW Botanical/Drug Interactions Goal Increase knowledge of botanicals and their interaction with other drugs Current Use Est. 18% of prescription drug users also use herbals, high-dose vitamin products, or both (1998) Designs Pre-clinical, Phase I and II trials Chemoprotection: Defense Against Toxins • Xenobiotics = foreign chemicals • Endobiotics = chemicals produced by body Inhaled Absorbed Ingested Synthesized monooxygenases conjugation enzymes transporters Liver Intestine CYP3A Induction Causes Drug Interactions • Expressed in liver and intestine • Bind to CYP3A promoter • Activated by xenobiotics and endobiotics Drug A “Inducer” ? XRE Rifampicin Dexamethasone Troglitazone Phenytoin Taxol St. John’s Wort? Kliewer et al. Drug B “Substrate” CYP3A CYP3A HO-Drug B excreted Indinavir Ethinylestradiol Atorvostatin Cyclosporin Warfarin Tamoxifen Doxorubicin Nuclear Receptor Superfamily N DNA Ligand C 48 NRs in human genome Classical Receptors Glucocorticoid Mineralocorticoid Progesterone Estrogen (a,b) Androgen Thyroid Hormone (a,b) Vitamin D all-trans Retinoic Acid (a,b,g) Kliewer et al. Orphan Receptors CAR PPAR (a,g,d) COUP (a,b,g) PXR DAX revErb (a,b) ERR (a,b,g) RXR (a,b,g) FXR ROR (a,b,g) GCNF1 SF1 (a,b) HNF4 (a,g) SHP LXR (a,b) Tlx NGFI-B (a,b,g) TR2 (a,b) PNR Northern blot Kliewer et al. heart brain placenta lung liver muscle kidney pancreas spleen thymus prostate testis ovary small intestine colon Human PXR Expression Pattern PXR Binds to CYP3A Promoter TGAACT caaagg AGGTCA <---------> CYP3A4 XRE PXR RXR XRE CYP3A PXR RXR Kliewer et al. - + + + - + 1 Kliewer et al. 7 5 .. sitosterol HO scopoletin Cell-based reporter assay umbelliferone hyperforin hyperoside rutin amentoflavone isoquercitrin quercitrin quercetin myricetin luteolin kaempferol pseudohypericin Hypericin extract 3 extract 2 extract 1 SR12813 rifampicin Fold activation St. John’s Wort Activates PXR O O 8 O 6 hyperforin 4 3 2 SJW Regulates Other PXR Target Genes 1 human hepatocytes • Phase II enzymes (conjugation) SULT1A1 • Transporters MDR1 Kliewer et al. solubilization • Phase I enzymes (oxidation) CYP3A4 CYP2B6 CYP2A4 ALDH1A4 excretion