* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
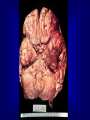
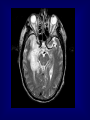
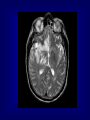
HERPES SIMPLEX ENCEPHALITIS M.RASOOLINEJAD, MD DEPARTMENT OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE TEHRAN UNIVERCITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE HERPES SIMPLEX ENCEPHALITIS ( HSE ) A SERIOUS ILLNESS WITH SIGNIFICANT RISKS OF MORBIDITY & MORTALITY TREATABLE ENCEPHALITIS EPIDEMIOLOGY Incidence: 1/ 250,000 to 500,000/ year Morbidity: Untreated patients, 70% Treated patients, 19% Morbidity: > 50% of survivors are left with moderate or severe neurologic deficits Sex: In male & female is equal Age: Peaks in childhood & middle-aged HSE Acute or Subacute Illness General & Focal Cerebral Dysfunction Sporadic Without Seasonal Pattern HSV-1 in 95% cases PATHOGENESIS Children & young adult: Primary HSV infection Olfactory bulb Adult: Prior HSV-1 infection ( Ab +ve ) Reactivation in Trigeminal or Autonomic roots Brain Brain PATHOLOGY Edema & Congestion & Hemorrhage &Necrosis Intense Hemorrhagic necrosis In Temporal & Frontal lobe Hallmark of HSE: Bilateral Asymmetrical Anterior Temporal lobe inflammation CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS NO PATHOGNOMONIC CLINICAL FINDING Typical symptoms: •Fever 90% •Headache 81% •Psychiatrics symptoms 71% •Seizures 67% •Vomiting 46% •Focal weakness 33% •Memory loss 24% •Altered mental status & photophobia CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS NO PATHOGNOMONIC CLINICAL FINDING Typical finding on P/E: •Alteration of consciousness 97% •Fever 92% •Dysphasia 76% •Seizures 38% (Focal 28%, General 10%) •Hemiparesis 38% •Cranial nerve defect 32% •Visual field loss 14% •Papilledema 14% DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS Brain abscess Epidural & Subdural abscess Neoplasms, Brain Pediatric febrile seizures Stroke & Hemorrhagic or Ischemic WORK-UP Lab Studies: CSF Mononuclear pleocytosis Elevated protein Nl or reduce glucose Initial may be Nl Hemorrhagic natureElevated RBC HSV is rarely cultured CSF/PCRSensitive & Specific WORK-UP Imaging Studies: MRI ( Preferred mainly imaging ) Bilateral Temporal & Inferior Frontal Changes CT-Scan ( much less sensitive than Other tests: EEG Focal abnormalities MRI ) Slow-wave or periodic sharp-wave Over temporal lobe Sensitive Not Specific TREATMENT Goals of therapy: 1.Shorten the clinical course 2.To prevent complications 1.To prevent subsequent recurrence TREATMENT ASYCLOVIR The drug of choice 10mg/kg (or 500mg/m2 ) IV q8h Each dose infused over 1 hour Duration: 10 to 14 days