* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 2: Drug and Alcohol Awareness
Survey
Document related concepts
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
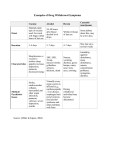
Module 2: Drug and Alcohol Awareness Objectives • To recognise own attitudes towards drugs and alcohol • To understand the reasons why people use drugs and alcohol • To be aware of the legality, effects, routes of use, and risks of alcohol, cannabis, cocaine and opiates Dual Diagnosis Capabilities • Non-Judgemental Attitude: Be aware of ones own attitudes and values in relation to dual diagnosis and be able to suspend judgement when working with service users, and carers. Challenge others’ attitudes in an appropriate and useful manner. Dual Diagnosis Capability 4 level 2 • Education and Health Promotion: Be able to offer basic but accurate and up to date information and advice about effects of substances on mental and physical health and vice versa. Dual Diagnosis Capability 8 level 2 Substance Use • Substances that alter level of consciousness and/or perception • Levels of use: – Experimental (occassional- not always safe!) – Recreational (regular, but within safe limits) – Bingeing/ dangerous use (high intensity over short length of time) – dependence (increased tolerance and withdrawals if stop) Exercise 1 Ask yourself these questions: • What attitudes do I have about people who use drugs and people who use alcohol? • Where did these attitudes come from? (Parents, school, media, religious beliefs etc) • How might these attitudes affect how I work with people with substance use problems? Exercise 2: Why Use? • Why do I (did I) smoke cigarettes; drink caffeinated drinks e.g. coffee, tea, cola; drink alcohol? Make a list of the reasons why, the benefits, and if there are any, some of the less good aspects of these habits. • why do people with mental health problems use drugs and alcohol? Make a list of the reasons that you are aware of from what service users have told you, or assumptions that you have made. Reasons for use • • • • • • • • • • • To feel euphoric or feel nothing To feel more confident To work longer hours or enhance performance To belong to a social group (peer pressure) To kill time (alleviate boredom) To alleviate physical pain and other health problems Because it is a habit To satisfy cravings and avoid withdrawal symptoms For weight loss To experience an altered state of consciousness To unwind after a stressful day Alcohol • Alcohol is a widely used, legal and socially acceptable drug. • It is taken orally. • It is a central nervous system depressant • Dangerous drug; accidents whilst intoxicated, overdose choking on vomit. • Alcohol related to 40% of violent offences;44 per cent for domestic violence and 53 per cent for violence committed against a stranger [British Crime Survey, 2000]. Alcohol 2 • Safe levels <3 units per day • Males up to 21 units/week; females up to 14 units/week • Unit = volume x ABV/1000 (250mls wine 13%ABV/1000=3.25 units • Physical dependency- ↑tolerance and withdrawals • Signs of withdrawal: nausea, vomiting, sweating, high temperature, hypertension, anxiety, sleeplessness, restlessness, and sometimes hallucinations, epileptic fits. • Withdrawals need immediate medical attention and treatment as can be life-threatening. • Never advise abrupt cessation of heavy drinking without treatment!! Cannabis • • • • • • • Cannabis is a sedative and hallucinogenic drug produced from the leaves and buds of the cannabis sativa plant. Most commonly used illegal drug. Cannabis is an illegal substance under class B of the misuse of Drugs Act. dried leaves or black/brown block of resin Cannabis leaves or resin are smoked (roll-up with tobacco or in a bong) Signs of Use: reddened eyes, dilated pupils, increased pulse rate, drowsiness, giggling, and a sweet herbal smell. Effects: relaxation, increased senses, slowing of thoughts, time seems to pass more slowly, sometimes mild hallucinogenic effects. Risks: mouth and lung cancer, exacerbate other lung conditions, increases likelihood of psychosis, road traffic accidents whilst driving under the influence. Cocaine and Crack Cocaine • • • • • • • Stimulant drugs Legality- class A drugs What do they look like: cocaine is a white crystalline powder, and crack is white or off-white crystalline rocks How taken: Cocaine may be taken orally, snorted, inhaled, or injected. Crack: inhaled from a pipe, but sometimes injected. Effects: Cocaine, in both forms, increases heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, thoughts and activity levels. It also lifts mood and gives a sense of energy and wellbeing. Signs of use: dilated pupils, dry mouth, elevated body temperature, teeth grinding, agitation, restlessness, excitability, pressure of speech, flight of ideas, weight loss (appetite suppressant). Risks: paranoia, confusion, and disorganized patterns of behaviour. The “come down” period causes fatigue, and depressed mood. Heart attacks, hgh blood pressure, stroke, and kidney damage Opiates • • • • • • • • • • Derived from the opium poppy. They include heroin, morphine, methadone and codeine. Central nervous system depressants Legality: these are class A drugs What they look like: heroin is a pale brown powder; also available in pharmaceutically manufactured form such as tablets, green or blue syrup (methadone) and glass ampoules (for injection) How used: mainly smoked or injected, some opiates are available in tablet and suppository form. Signs of use: pallor, pinprick pupils “pinned”, sedation/drowsiness (“gouching out”), signs of injecting on body Effects: people feel emotionally numb, warm and drowsy, with an initial intense rush, especially if injected intravenously. Withdrawals: gooseflesh, shivering, profuse sweating, feeling feverish, aching limbs, yawning, runny eyes, runny nose, gastrointestinal disturbances such as stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea. Risks: overdose, injecting related problems, BBVs, accidents Other Drugs: solvents, ecstasy, LSD, amphetamines Other Drugs • Hallucinogens: LSD, magic mushrooms – Distort perceptions for several hours – “psychotic” trip – Can be terrifying “bad trip” • Ecstasy – – – – • Stimulant and mildly hallucinogenic Feelings of empathy, energy Depression and short term memory problems Death as a result of kidney failure Amphetamines – Effects like cocaine – Paranoia and aggression • Solvents and gases – Sniffed, inhaled – Intoxication – Risk of instant death, brain damage, accidents • Caffeine– “Red Bull”; coffee; cola drinks – Stimulants, irritability, aggression, paranoia • • OTC- over the counter (cough linctus, anti-histamines etc) Prescription drugs- benzodiazepines, anti-cholinergics