* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Probability - University of Central Missouri
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
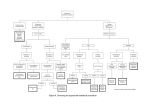
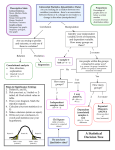
MORE on ANOVA What is an Error Term? What is a Mixed ANOVA? What is a Three-Way ANOVA? What is a Three-Way Interaction? Why Should You Be Careful about Higher-Order ANOVAs? What is an Error Term? • The denominator of the F-test in any ANOVA is also called the error term. • In different types of ANOVA, the error term is calculated differently. • The error term always contains only nonsystematic variance. What is a Mixed ANOVA? • Factorial ANOVA with at least one between-subjects factor and at least one within-subjects factor. • Dividing the variance becomes more complicated. • The F-tests are interpreted in the same way. What is Three-Way ANOVA? • Factorial ANOVA with three factors. • All combinations of levels of all three factors are measured. • Can be between subjects, within subjects, or mixed. 1 A 2 1 B 1 2 1 A C 2 1 B 2 2 Effects Tested in a Three-Way ANOVA • • • • • • • Main Effect of A Main Effect of B Main Effect of C AxB Two-way Interaction AxC Two-way Interaction BxC Two-way Interaction AxBxC Three-way Interaction What is a Three-Way Interaction? • A two-way interaction that changes depending on the level of a third factor. • Example: For inpatients, the effect of the drug is greater for people getting cognitive than behavior therapy. For outpatients, the effect of the drug is greater for people getting behavior therapy. Drug Placebo Drug Prozac Placebo Prozac 20 40 20 60 20 60 20 40 Inpatient Outpatient Setting Why Should You be Careful about Higher-Order ANOVAs? • You must always interpret the most complex effect that is significant. • Results of higher-order ANOVAs become difficult to interpret. • “Never eat anything bigger than your head.”