Updating Empiricist Mentalist Semantics
... sentences and parse them into electronic texts. They can even pronounce sentences in such a way that humans can understand them. This is already a great achievement, but the computers executing these tasks have no sense of what they are processing or producing; they completely fail to grasp its mea ...
... sentences and parse them into electronic texts. They can even pronounce sentences in such a way that humans can understand them. This is already a great achievement, but the computers executing these tasks have no sense of what they are processing or producing; they completely fail to grasp its mea ...
A QUALITATIVE EXPLORATION OF EMOTIONAL RESPONSES OF
... friendships. There are three different types of mania. Euphoric mania, which make people appear happier and very excited about anything (Belmaker, 2004). Patients in these episodes can have a substantial influence on other people because of high positive energy and self-confidence. However, they may ...
... friendships. There are three different types of mania. Euphoric mania, which make people appear happier and very excited about anything (Belmaker, 2004). Patients in these episodes can have a substantial influence on other people because of high positive energy and self-confidence. However, they may ...
How Do We Know That We Know? The Accessibility Model
... In the present article, I focus on one general cue for the FOK: the accessibility of pertinent information. According to the position advanced in this article, the cues for the FOK are to be found in the very information that is activated or accessed during the course of the search-and-retrieval pro ...
... In the present article, I focus on one general cue for the FOK: the accessibility of pertinent information. According to the position advanced in this article, the cues for the FOK are to be found in the very information that is activated or accessed during the course of the search-and-retrieval pro ...
SR associations, their extinction, and recovery in an animal model of
... Rachman, 1977, 1990). However, it is not clear why something learned by vicarious or instructional processes would not be remembered as a cause of the phobic reaction. Thus, the associative account still fails to explain some patients’ failure to remember the source of phobias. An associative accoun ...
... Rachman, 1977, 1990). However, it is not clear why something learned by vicarious or instructional processes would not be remembered as a cause of the phobic reaction. Thus, the associative account still fails to explain some patients’ failure to remember the source of phobias. An associative accoun ...
Negative affect induced by derogatory verbal feedback modulates
... the beginning of an experiment. An ERN relationship to trait, but not to state variables like anger, tension and fatigue has been reported by Tops et al. (2006). Although subjects scored higher on the post-experimental state variables tiredness and anger, this was not correlated to ERN amplitude. In ...
... the beginning of an experiment. An ERN relationship to trait, but not to state variables like anger, tension and fatigue has been reported by Tops et al. (2006). Although subjects scored higher on the post-experimental state variables tiredness and anger, this was not correlated to ERN amplitude. In ...
Verplanck
... and "concept-formation" that the wnter had been doing In these, while seemmg to behave m conformity with continuity theory, the subjects always did a lot of "hypothesizmg" (agam, some of it to the pomt) k la the Tohnan-Krechevsky school Even the wnter, resent it though he may (as a Spencian mcrement ...
... and "concept-formation" that the wnter had been doing In these, while seemmg to behave m conformity with continuity theory, the subjects always did a lot of "hypothesizmg" (agam, some of it to the pomt) k la the Tohnan-Krechevsky school Even the wnter, resent it though he may (as a Spencian mcrement ...
Within-subjects Extinction and Renewal in Predictive Judgments
... effect, and has received important empirical support using animals as subjects (v.g., Bouton & Bolles, 1979; Rosas & Bouton, 1997b; see Bouton, 1993 for a review). Renewal has been also found when acquisition and extinction are conducted in the same context, and the test is run in a different one (v ...
... effect, and has received important empirical support using animals as subjects (v.g., Bouton & Bolles, 1979; Rosas & Bouton, 1997b; see Bouton, 1993 for a review). Renewal has been also found when acquisition and extinction are conducted in the same context, and the test is run in a different one (v ...
Attention and Resistance To Extinction
... Last Trial on which a GSR occurred tor all subjects (ranked) •••••••••••• ...
... Last Trial on which a GSR occurred tor all subjects (ranked) •••••••••••• ...
Pavlovian Contingencies and Temporal Information
... Second, we used an algorithm that finds change points in cumulative records (Gallistel, Fairhurst, & Balsam, 2004). First, we computed the cumulative record of responses versus trials. If the average rate (responses per trial) remains constant, then the slope of the cumulative record will be constan ...
... Second, we used an algorithm that finds change points in cumulative records (Gallistel, Fairhurst, & Balsam, 2004). First, we computed the cumulative record of responses versus trials. If the average rate (responses per trial) remains constant, then the slope of the cumulative record will be constan ...
Affect and psychological magnification: Denvations from Tomkins
... predicted that interpersonal themes are more frequent in scenes based on joy as compared with excitement, and shame as compared with fear. Differential magnification of positive and negative affects. Tomkins (1979) distinguishes two different cognitive processes involved in the magnification of posi ...
... predicted that interpersonal themes are more frequent in scenes based on joy as compared with excitement, and shame as compared with fear. Differential magnification of positive and negative affects. Tomkins (1979) distinguishes two different cognitive processes involved in the magnification of posi ...
Rodolphe Gouin - Hal-SHS
... wrong answers to the questions asked. “Why are the reasons of the subjects perceived as good when their answers are wrong ? It is because they tried to answer the questions they were confronted with by making a guess, a conjecture, or by applying a theory or a general principle valid in many cases.” ...
... wrong answers to the questions asked. “Why are the reasons of the subjects perceived as good when their answers are wrong ? It is because they tried to answer the questions they were confronted with by making a guess, a conjecture, or by applying a theory or a general principle valid in many cases.” ...
C) Pathos!!! - Mrs. Mehrens` English Page
... B) Prejedice C) Prejidice D) Prejudice E) Prejudace ...
... B) Prejedice C) Prejidice D) Prejudice E) Prejudace ...
Trait Conceptualization and Measurement of
... Richins and Dawson were not the first to classify materialism as a value however. In their classic work, Csikszentmihalyi and Rochberg-Halton (1981) discuss materialism as a value and differentiate between instrumental materialism and terminal materialism. Under instrumental materialism, individual ...
... Richins and Dawson were not the first to classify materialism as a value however. In their classic work, Csikszentmihalyi and Rochberg-Halton (1981) discuss materialism as a value and differentiate between instrumental materialism and terminal materialism. Under instrumental materialism, individual ...
Similarity and Distance in Information Spatializations Sara Irina
... appears a little longer as compared to the same distance within regions. In agreement with the results for point displays, however, similarity judgments in network and region displays are more variable than distance judgments. Our findings provide much needed empirical evidence on the conditions und ...
... appears a little longer as compared to the same distance within regions. In agreement with the results for point displays, however, similarity judgments in network and region displays are more variable than distance judgments. Our findings provide much needed empirical evidence on the conditions und ...
Psychology 100.18
... • The Wason selection task – Within a familiar content > You are working at a bar > There is a table of 4, each person is drinking something, you can see that one person is drinking beer, another is drinking Coke. > You know the other two people,one is 18, one is 19 yrs old. If one is drinking beer, ...
... • The Wason selection task – Within a familiar content > You are working at a bar > There is a table of 4, each person is drinking something, you can see that one person is drinking beer, another is drinking Coke. > You know the other two people,one is 18, one is 19 yrs old. If one is drinking beer, ...
Probability - University of Central Missouri
... • A two-way interaction that changes depending on the level of a third factor. • Example: For inpatients, the effect of the drug is greater for people getting cognitive than behavior therapy. For outpatients, the effect of the drug is greater for people ...
... • A two-way interaction that changes depending on the level of a third factor. • Example: For inpatients, the effect of the drug is greater for people getting cognitive than behavior therapy. For outpatients, the effect of the drug is greater for people ...
Consciousness, Learning, Cognition and Language Test 1. A two
... (C) minimize the overconfidence phenomenon. (D) involve greater reliance on language skills. (E) avoid the issue of functional fixedness. ...
... (C) minimize the overconfidence phenomenon. (D) involve greater reliance on language skills. (E) avoid the issue of functional fixedness. ...
Generalisability
... forgetting works according to the cue dependency theory (context dependent forgetting) should be the same for everyone – this means that we can generalise from the study to the way most people’s ...
... forgetting works according to the cue dependency theory (context dependent forgetting) should be the same for everyone – this means that we can generalise from the study to the way most people’s ...
The stress model of Yerkes-Dodson law suggests that at low and
... students were asked to fill out the computerized questionnaire, which had true or false statements reflecting back on the video clip. Statements were different for each condition, and they required a yes or no response (‘Y’ or ‘N’ on computer keyboard) from the participant. After approximately an ho ...
... students were asked to fill out the computerized questionnaire, which had true or false statements reflecting back on the video clip. Statements were different for each condition, and they required a yes or no response (‘Y’ or ‘N’ on computer keyboard) from the participant. After approximately an ho ...
Final Review Guide ( Due on May 2-counts toward
... How can the confirmation bias and fixation block our ability to effectively problem solve? How does the availability heuristic affect our social judgment? Representative Heuristic? What is the difference between belief bias and belief perseverance? Be sure to explain. Explain the three beginning sta ...
... How can the confirmation bias and fixation block our ability to effectively problem solve? How does the availability heuristic affect our social judgment? Representative Heuristic? What is the difference between belief bias and belief perseverance? Be sure to explain. Explain the three beginning sta ...
Brain Teasers - Dartmouth Math Home
... Therefore, we would recommend that future projects be performed on a large population of students from many different grade-levels and institutions, that a more time-oriented cognitive task be chosen, and that the subjects be truly isolated in the testing situation. ...
... Therefore, we would recommend that future projects be performed on a large population of students from many different grade-levels and institutions, that a more time-oriented cognitive task be chosen, and that the subjects be truly isolated in the testing situation. ...
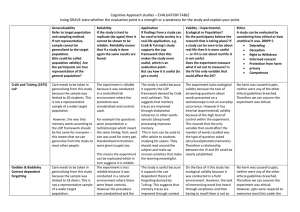
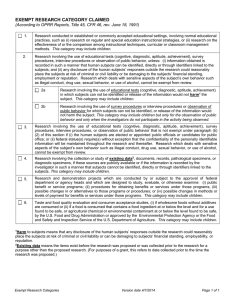
EXEMPT CATEGORY CLAIMED
... effectiveness of or the comparison among instructional techniques, curricular or classroom management methods. This category may include children. Research involving the use of educational tests (cognitive, diagnostic, aptitude, achievement), survey procedures, interview procedures or observation of ...
... effectiveness of or the comparison among instructional techniques, curricular or classroom management methods. This category may include children. Research involving the use of educational tests (cognitive, diagnostic, aptitude, achievement), survey procedures, interview procedures or observation of ...
Construction of mental model in mechanics through sensory
... interpretations. The observed responses reflected three cognitive mechanisms: sharing of sensory information, using strategies of scientific inquiry and using mental images of forces and motion. These mechanisms contributed to the representation of physics ideas. Along with alternative ideas such as ...
... interpretations. The observed responses reflected three cognitive mechanisms: sharing of sensory information, using strategies of scientific inquiry and using mental images of forces and motion. These mechanisms contributed to the representation of physics ideas. Along with alternative ideas such as ...