* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Financial Management
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
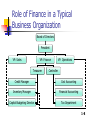
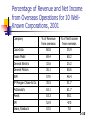
CHAPTER 1 - B&H An Overview of Financial Management Pankaj Agrrawal, Ph.D. Career Opportunities Issues of the New Millennium Forms of Businesses Goals of the Corporation Agency Relationships 1-1 Better than avg. drivers, pls. stand up. Finance Concepts are Simple, the Behavioral Aspects are not… A $ today is better than a $ tomorrow (concept of TVM) Buy Low sell High (arbitrage – fear and greed, I say fear of losing and missing are the only motivators) No free lunch (the world of risk and return, CAPM, APT) Prices do not instantaneously adjust to all new information (random price path irrationality) 1-2 Let’s take a 5-7 minute “Initial” Exam: PA: If you can get an asset worth $100 for $90, what’s the instant profit you just made? If your initial investment declines by 50%, what percentage increase will bring you back to even? If the average annual returns for the past two years has been –50% and +50%, what is the return on your investment over those two years? If your investment has trebled in value, what is the associated percentage rise? 1-3 Financial Management Issues of the New Millennium The effect of changing technology: lower costs, efficient, barriers to entry lowered The globalization of business 1-4 Relevance of Finance and Globalization: If you are a Doctor / Engineer– how does FM affect you? For self decisions – day to day Good business organization If you are a Nebraska Homebuilder– how does Globalization affect you? (discuss KO) Interest rates –global- housing demand Local economy – wheat demand - global 1-5 Career Opportunities in Finance Money and capital markets Financial management Investments Financial Intermediaries: Banking Corporate Finance: Managing the financing of corporations Investment Management: Portfolio Management 1-6 1-7 Role of Finance in a Typical Business Organization Board of Directors President VP: Sales VP: Finance Treasurer VP: Operations Controller Credit Manager Cost Accounting Inventory Manager Financial Accounting Capital Budgeting Director Tax Department 1-8 Responsibility of the Financial Staff Maximize stock value by: Forecasting and planning Investment and financing decisions Coordination and control Transactions in the financial markets Managing risk 1-9 Percentage of Revenue and Net Income from Overseas Operations for 10 WellKnown Corporations, 2001 Company % of Revenue from overseas % of Net Income from overseas Coca-Cola 60.8 35.9 Exxon Mobil 69.4 60.2 General Electric 32.6 25.2 General Motors 26.1 60.6 IBM 57.9 48.4 JP Morgan Chase & Co. 35.5 51.7 McDonald’s 63.1 61.7 Merck 18.3 58.1 3M 52.9 47.0 Sears, Roebuck 10.5 7.8 1-10 Alternative Forms of Business Organization Sole proprietorship Partnership Corporation 1-11 Sole proprietorships & Partnerships Advantages Ease of formation Subject to few regulations No corporate income taxes Disadvantages Difficult to raise capital Unlimited liability Limited life 1-12 Corporation Advantages Unlimited life Easy transfer of ownership Limited liability Ease of raising capital Disadvantages Double taxation (Delaware 300k+ companies) Cost of set-up and report filing 1-13 Financial Goals of the Corporation The primary financial goal is shareholder wealth maximization, which translates to maximizing stock price. Do firms have any responsibilities to society (safety, pollution, antitrust- price gouging,fair hiring) at large? (DSEFX [ETF=KLD-show how to locate], SPX, VICEX – 3yrs) Priced out of mkt Shunned by investors Social objectives have to be mandated – role of Govt Is stock price maximization good or bad for society (efficient production, new technology,new jobs)? Should firms behave ethically? 1-14 1-15 Is stock price maximization the same as profit maximization (Rev-Cost)? No, despite a generally high correlation amongst stock price, EPS, and cash flow. Current stock price relies upon current earnings, as well as future earnings and cash flow. Some actions may cause an increase in earnings, yet cause the stock price to decrease – risk impact (and vice versa). 1-16 Agency relationships An agency relationship exists whenever a principal hires an agent to act on their behalf. Within a corporation, agency relationships exist between: Shareholders and managers Shareholders and creditors 1-17 Shareholders versus Managers Managers are naturally inclined to act in their own best interests (ICC). But the following factors affect managerial behavior: Managerial compensation plans Direct intervention by shareholders (free rider problem – Satellite Dish example) The threat of firing The threat of takeover (poison pills, greenmail) 1-18 Shareholders versus Creditors Shareholders (through managers) could take actions to maximize stock price that are detrimental to creditors. In the long run, such actions will raise the cost of debt and ultimately lower stock price. 1-19 Factors that affect stock price Projected cash flows to shareholders Timing of the cash flow stream Riskiness of the cash flows 1-20 Basic Valuation Model CF1 CF2 CFn Value 1 2 (1 k) (1 k) (1 k)n n CFt . t t 1 (1 k) A=P(1+r)^n => 110 = 100(1+10%) ^1 yr For 2 years CF is: 10/(1.1)+(10% of 100)/(1.1*1.1)+100/(1.21) = (11+10+100)/1.21 =>100 Or 9.09+10/1.21+100/1.21= 9.09+8.26+82.64 =>99.99 (A $ one yr from now is more valuable than two yrs from now) To estimate an asset’s value, one estimates the cash flow for each period t (CFt), the life of the asset (n), and the appropriate discount rate (k) Throughout the course, we discuss how to estimate the inputs and how financial management is used to improve them and thus maximize a firm’s value. 1-21 Factors that Affect the Level and Riskiness of Cash Flows Decisions made by financial managers: Investment decisions Financing decisions (the relative use of debt financing) Dividend policy decisions The external environment 1-22 Austrian Economic Cycle Liquidity is the fuel behind financial market fluctuations BOND (Liquidity flows out of bonds and into stocks and then the real economy) PRICES FALL INFLATION RISES SHORT-TERM INTEREST RATES RISE STOCK PRICES Capacity constraints FALL hit. Employment PROPERTY greater than natural PRICES level. Leading inflation gauge up. Industrial FALL production high. RECESSION INFLATION BOND RISES PRICES FALL ECONOMIC RECOVERY STOCK PRICES RISE Economic variables begin over heating Earnings growth strong. BOND PRICES RISE Industrial commodity prices soften GDP growth decreases, economic variables weaken. Industrial commodity prices begin to strengthen SHORT-TERM RATES FALL INFLATION FALLS Economic variables look very weak The cycle depicts when liquidity is rising or falling. An expansion in liquidity during disinflation washes through the most liquid assets first and then into the economy. 6 Year Cycle 1-23 HW Questions Ch 1: 1-1, 1-5, 1-6, 1-7, 1-8 and ST -1 (solutions at end of book, in Appx B)---- Read Ch 4, self review ST questions page 159 1-24