* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Global Marketing
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
State capitalism wikipedia , lookup
Protectionism wikipedia , lookup
Non-simultaneity wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Market socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Uneven and combined development wikipedia , lookup
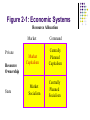
The Global Economic Environment Chapter 2 Global Marketing Figure 2-1: Economic Systems Resource Allocation Private Resource Ownership State Market Command Market Capitalism Centrally Planned Capitalism Market Socialism Centrally Planned Socialism Market Capitalism Economic system in which individuals and firms allocate resources: Production resources are privately owned Consumers decide what goods are desired Firms determine what and how much to produce Centrally Planned Socialism Total opposite of market capitalism (ex: North Korea) State plans and decides what goods and services are produced and in what quantities Consumers can spend on what is available Centrally Planned Capitalism Economic system in which command resource allocation is used extensively in an environment of private resource ownership Market Socialism Economic system in which market allocation policies are permitted within an overall environment of state ownership Which system is the best one? Canada: Government revenues rose from 29 to 43 percent of GDP between 1966 and 1996. This rise in revenues was almost entirely accounted for by a massive rise in personal income tax, from 9 to 20 percent of GDP Extensive social security network Spend-and-tax policy resulted in some loss of international competitiveness Source: Fraser Institute Index of Economic Freedom by the Heritage Foundation, 2003 Ranking of Economic Freedom (out of 161 economies) 1 Hong Kong 1.45 (free) 2 Singapore 1.50 6 United States 11 Netherlands 18 Canada 19 Belgium 20 Germany 35 Japan 40 France 44 Hungary 52 Korea 56 Mexico 1.80 1.90 2.05 (mostly free) 2.10 2.10 2.50 2.55 2.65 2.70 2.80 OECD: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development 29 nations each with market-allocation economic systems G-8 (G-7 plus Russia) Leaders from these high income countries work to establish prosperity and ensure monetary stability United States Japan Germany France Britain Canada Italy The Triad Dominant economic centers of the world Divisions in research or business organizations 1. Japan 2. Western Europe 3. United States Expanded Triad 1. Pacific Region 2. European Union (EU) 3. NAFTA Balance of Payments (BOP) Recording all economic transactions between the residents of a country and the rest of the world 1. Current account – record of all recurring trade in merchandise and services, private gifts, and public aid between countries trade deficit – negative BOP trade surplus – positive BOP (Canada) 2. Capital account – record of all long-term direct investment, portfolio investment, and capital flows