* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1.12 - Economic Threats
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Balance of trade wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
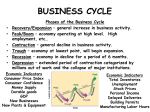
BUSINESS AND MANAGEMENT MODULE 1 BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS & ENVIRONMENT Economic Opportunities & Threats Refers to large scale economic factors affecting the economy as a whole – Government policies – Attitudes and actions in foreign countries – Business and consumer confidence Macroeconomic Objectives Governments objectives: tend to have four – Control inflation – Economic growth – Reduce unemployment – Acceptable international trade balance Controlled Rate of Inflation A continual rise in the general prices of the economy Most countries regard a low or sustainable inflation rate as a necessity for achieving the other economic objectives There are two main causes of inflation Demand Pull Inflation Caused by excessive aggregate demand in the economy – Any factor that causes a rise in consumption, investment, government spending or trade will lead to an increase in aggregate demand If consumer confidence is high, this encourages people to spend money, and firms to spend money on production Cost Push Inflation Caused by higher production costs leading to a rise in prices (assuming firms want to maintain their profit margins) – Union wage increases – Material costs – Affects of climate on crops Controlling Inflation By limiting demand-pull and cost-push factors – Domestic government might raise taxes to control the amount of consumption in the economy – It could subsidize local businesses to reduce costs of production – Could pursue “supply-side policies” that improve the productive capacity of the economy (investment in health care/education etc) – Exercise 10 – Zimbabwe’s Inflation Problems Unemployment Measures the proportion of a country’s workforce not in employment Influenced by aggregate demand – as production is high, unemployment will be low Economic costs of unemployment affect both the government and society Unemployment Solutions Demand-side policies – Directly target increasing the level of aggregate demand Reducing taxes or increasing government spending Reducing interest rates Supply-side policies – Increase the level of aggregate supply – Tend to be more permanent policies Types of Unemployment Frictional – time lapse between leaving one and finding another Seasonal – caused by seasonal change Technological – losing a job to automation Regional – analysis of different areas (urban vs rural) Structural – a particular industry suffers Cyclical – recessionary unemployment; affecting everyone Economic Growth Refers to an increase in a country’s economic activity over time Measured by the change in total output known as the GDP Changes in the economic pattern are typically known as cycles There are several key phases The Business Cycle GDP ($) Trend line Peak Recession Recovery Economic Activity Slump Time Trading Cycle Peak – economic activity is at its highest level – Consumer spending and investment is high; low unemployment; good cash flow Recession – dip in level of economic activity for two successive quarters – Declining aggregate demand; falling exports and lower investment Slump – bottom of a recession (last decline stage) – High unemployment and low levels of consumer spending; poor cash flow and high bankruptcy rates Recovery – level of GDP starts to rise again – Consumption, spending and investment begin to rise Mini Case Study Case Study – ASOS Source: Jones, Hall, Raffo, Business Studies 3rd Edition, Unit 3, page 37 Coping with a Recession Cost reduction – Efforts to cut utility bills; cheaper warehousing; staff reductions Price reduction – Influence consumer spending Non-pricing strategies – Repackaging, special offers, after-sales care Branding – Consumers maintain loyalty to a brand even during recessionary times; price elasticity Outsourcing – Lower production costs overseas can help maintain a businesses profit level Barriers to Economic Growth Lack of infrastructure – Basic electricity, roads, hospitals etc Lack of technical knowledge Rapid population growth – High net birth results in too many mouths to feed, which may hinder economic development High foreign debt repayments – Countries are obliged to meet interest and debt repayments first leaving little for domestic growth Balance of Payments A record of a country’s money inflows and outflows (over a specific time) Made up of a capital account and current account – Current Export and import earnings and expenditures – Capital Government services, foreign currency etc Current Account Visible trade balance – International trade in tangible goods (oil, steel cars etc) Invisible trade balance – Intangible goods such as banking, distribution and insurance Exchange Rates Measures the value of one currency in terms of another foreign currency A higher rate (appreciation of currency) means that export prices will be relatively higher, thereby reducing competitiveness A lower rate (depreciation of currency) means that domestic firms that import raw materials will suffer from having to pay higher prices Governments try to protect the balance of payments by adjusting exchange rates (through interest rate changes) – Exercise – Exchange rates Protecting Against Currency Fluctuations Large fluctuations in exchange rates can create difficulties for businesses Cannot accurately forecast import requirements (costs) International deals may be postponed until currency fluctuations are minimized Protectionism – Government policy used to safeguard domestic business – Involves tariffs or quotas for example Examples of Protectionism Tariffs – Form of tax placed on imported products; gives domestic goods a slight advantage Quotas – Quantitative limits that prevent too many foreign products entering a country Subsidies – Payments made by government to a domestic business as a form of aid Embargos – Physical bans on international trade with certain countries Standards – Imposition on strict standards (health and safety) on certain imported products