* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basics of Economics - Solon City Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
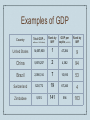
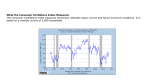
Basics of Economics Key terms and ideas Economic Indicators ❖ The strength or weakness of an economy is often measured by “economic indicators” - pieces of data that relate whether the economy is expanding or contracting Gross Domestic Product ❖ The market value of the all goods and services produced in a country in a given period of time ❖ “per capita” = “for each head” = per person ❖ Is an indicator of a country’s standard of living Examples of GDP Country Total GDP (in millions of U.S. dollars) Rank by IMF GDP per capita (in U.S. $) Rank by IMF United States 14,657,800 1 47,284 9 China 5,878,257 2 4,382 94 Brazil 2,090,314 7 10,816 53 Switzerland 523,772 19 67,246 4 Zimbabwe 5,574 141 594 163 Unemployment Rate ❖ According to the U.S.Bureau of Labor Statistics: Persons are classified as unemployed if they do not have a job, have actively looked for work in the prior 4 weeks, and are currently available for work. Persons who were not working and were waiting to be recalled to a job from which they had been temporarily laid off are also included as unemployed. Receiving benefits from the Unemployment Insurance (UI) program has no bearing on whether a person is classified as unemployed. ❖ July 2011 - United States: 9.1% ❖ June 2011 - Ohio: 8.8% ❖ Unemployment Rate Graph Inflation ❖ Inflation measures the value of a country’s currency over time ❖ Usually a measure of the RISE in prices for goods or services ❖ Let’s try it! Calculate Inflation Rates Inflation ❖ The Federal Reserve Board will try to curb inflation by limiting the amount of money that is circulating in the economy. ❖ When too much money is in circulation, the value of each bill will decrease, thus costing MORE to purchase goods. Interest Rates ❖ An “interest rate” is the percentage at which a loan is repaid to the lender ❖ For example, when people get a mortgage (loan for a house) they pay the bank the total amount borrowed PLUS a percentage of the total mortgage amount Interest Rates ❖ The Federal Reserve also influences interest rates ❖ The Federal Reserve is the “banker’s bank” - it lends money to banks at a “discount rate” = interest rate for banks ❖ When the discount rate is lowered, banks can offer customers lower interest rates and still make a profit ❖ This usually provides an economic “boost” Consumer Price Index (CPI) ❖ a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services. ❖ Whose buying habits does the CPI reflect? The CPI reflects spending patterns for each of two population groups: all urban consumers and urban wage earners and clerical workers. The all urban consumer group represents about 87 percent of the total U.S. population. It is based on the expenditures of almost all residents of urban or metropolitan areas, including professionals, the selfemployed, the poor, the unemployed, and retired people, as well as urban wage earners and clerical workers. Not included in the CPI are the spending patterns of people living in rural nonmetropolitan areas, farm families, people in the Armed Forces, and those in institutions, such as prisons and mental hospitals. Consumer inflation for all urban consumers is measured by two indexes, namely, the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) and the Chained Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (C-CPI-U). (from www.bls.gov) ❖ Let’s Look at the CPI! Housing Data ❖ A final economic indicator is “housing data;” it includes the following: ❖ 1) foreclosure rates ❖ 2) new construction ❖ 3) real estate transfers