* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Business Cycle
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Helicopter money wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
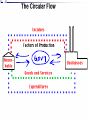
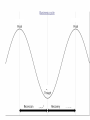
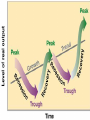
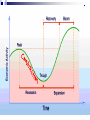
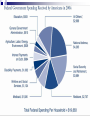
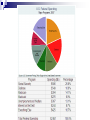
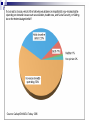
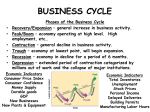
Unit 2: The Government, Banking and the Economy Who in government has the responsibility to respond when the economy is in trouble? The President? Congress? The Fed? Keeping watch over… THE BUSINESS CYCLE Business cycle The Business Cycle Contraction vs. Expansion Peak vs. Trough Recession vs. Depression Recession Characteristics… 2 Quarters declining GNP 6-18 months unemployment rates rise stable (or declining) prices Why & How does this happen? Variables that determine the Business Cycle… WHY ??? Business Investments Interest rates & Credit Consumer expectations External shocks Business Investments Investment spending increases GDP and maintains expansion - growth Business cuts leads to a decline in aggregate (total) demand & GDP slows/contractsrecession Business cuts causes a reduction in output & income in other sectors & GDP slows/contracts- recession Interest Rates & Credit Business and consumers’ spending are influenced by rates and availability of credit As rates climb, or loans become hard to get, spending and investment dries up, as does job growth (CONTRACTION – RECESSION) This is what happened throughout 2009 after many big banks collapsed! Consumer expectations Expectations breed fear or hope… Consumers expect layoffs – stop spending! Consumers expect raises – spend more! Consumer expectations become selffulfilling prophesies External shocks Some factor indirectly has an impact on the economy… Drought, war, oil embargo, etc. can affect aggregate supply As supply changes, so does production and price, thus impacting GDP (1970s OPEC Oil crisis) Who in government has the responsibility to respond when the economy is in trouble? The President? Congress? The Fed? Monetary Policy Controlled by the Federal Reserve The Bank for Banks Board of Governors, Janet Yellen Regional Banks Goal: To expand or contract the amount of money in supply so as to control spending and inflation and manage the business cycle Three Methods Interest rates Open Market Operations Reserve requirement 2009 http://www.pbs.org/newshour/makingsense/how-candid-should-janet-yellen-bewatching-emerging-markets-overreact-tofed-transparency/ Monetary Policy The Federal Reserve’s attempt to control the business cycle How… track the economic indicators, and control the amount of money in supply how does the FED know when these events are taking place?? Economic Indicators Economic Indicators Unemployment Types: Frictional (always exists) seasonal structural (changing society) cyclical (accd. to business cycle) Inflation Changes to the Consumer Price Index Economic Growth Gross National / Domestic Product Define the three methods of Monetary Policy… Open Market Operations Discount rate Reserve requirement Interest Rates (Discount Rate) The rate the Fed charges banks to borrow money Lower the rate – expansionary Raise the rate - contractionary Interest Rates Mortgage Calculator Open Market Operations The Fed’s buying and selling of US securities (bonds) to add or subtract from the reserves of the nation’s banking system Purchase of bonds – expansionary Sale of bonds - contactionary Reserve Requirements The fraction of money (based on total money) banks are required to keep on reserve The amount of money banks ‘have on hand’ – or can’t loan out to borrowers Set as a % Lower the percentage – expansionary Raise the percentage – contractionary Practice scenarios… 7% Inflation 4% Unemployment 3% GNP Growth Rate 6 % Inflation 9 % Unemployment 10% Unemployment -2% GNP Growth 2 %inflation FISCAL POLICY Other alternatives… Who else is responsible? Fiscal Policy Congress/President adjust federal taxes and federal spending Meant to control aggregate demand and sometimes aggregate supply Like monetary policy, it can be expansionary or contractionary Intended to monitor and adjust the Business cycle Circular flow…includes the government… When and how does the Government enact an expansionary fiscal policy? When? During a Recession or … high unemployment, low business and consumer spending, declining GNP How? Government raises aggregate demand by becoming a major consumer (spending) Government cuts taxes, thus raising aggregate demand, or allowing people more disposable income Problems/Controversy? National debt/deficit Where is the money going? When and how does the Government enact an contractionary fiscal policy? When? Economy is growing quickly – Inflation results How? Government lowers aggregate demand by cutting government spending Government raises taxes, thus lowering aggregate demand, or decreasing the amount of personal disposable income Problems/Controversy? What programs should be cut by the government? Examining trends U.S. federal spending as a percentage of gross national product from 1790 to 1990.