* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HSB 4M
Structuralism wikipedia , lookup
Intercultural competence wikipedia , lookup
American anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Structural anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Political economy in anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness in humans wikipedia , lookup
Social Bonding and Nurture Kinship wikipedia , lookup
Social anthropology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural anthropology wikipedia , lookup
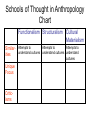
HSB 4M Chapter 1 Homework Review Definitions - Matching Anthropology “organization developed to meet society’s basic needs.” Culture “Its goal is to develop a broad and comprehensive understanding of what it means to be human.” Sociology “The systematic study of human social life, groups, and societies.” Social “The learned patterns of behaviour Institution and thought that help a group adapt to its surroundings.” Headings in Notes? • What was the title of the section of the chapter that covered pages 6-8? History of Globalization in Brazil • Globalization is simply increased trade links between countries. • What happened to Brazil’s economy since the 1950s? – Mechanization on large sugar plantations – Less subsistence farming – GDP per capita increased Social Effects of Globalization • One’s intuition might lead to thinking that all of Brazil benefited from the economic changes. – What happened in “Bom Jesus” as a result of the economic changes? • Diet changed • Infant mortality rate very high (stats) • Other Scheper-Hughes’ Research Methods • How did she collect her data? • How did she learn from the women? – What safeguards did she use to protect them and encourage them to be forthcoming with their stories? Key Concept Connections • Which key concepts connect to the Bom Jesus case study other than the one bolded (GDP per capita)? – Participant observation – Anthropology – Culture – Behaviour Family Tree American Nuclear Family Ju/Wasi Camp Trobriand Island Ethnography • What is it? • Who uses it? Kinship Matching Mating ___ A) Descent Birth ___ B) Marriage Nurturance ___ C) Adoption Kinship con’t • A family friend you call “auntie” is an example of: • How could you tell if a family is matrilineal or patrilineal? Challenges of Kinship in a Diverse Society • In groups, take these scenarios and rank them most (1) to least (7) in terms of the challenge they pose in the multicultural society of Canada. A: Same-sex marriage B: Same-sex marriage spouses adopting children or using a surrogate mother C: Cohabitation D: Blended families E: Intercultural marriages F: Arranged marriages G: Children being raised abroad by their grandparents Schools of Thought • Are schools of thought the same as disciplines? • How are they the same or different? Schools of Thought in Anthropology Chart Functionalism Structuralism Cultural Materialism Attempts to Attempts to Similar- Attempts to understand cultures understand cultures understand ities cultures Unique Focus Criticisms Schools of Thought in Anthropology, con’t • For each of the following, indicate whether it matches with Functionalism (A), Structuralism (B), or Cultural Materialism (C) • • • • • • • • • __ Learn how good or bad are defined in context. __ Every practice has a purpose. __ Infrastructure; structure; superstructure and technology. __ Technology and economy determine what a society will be like. __ Institutions serve the best interest of the majority. __ Overlooks negative results of some practices. __ May try to fit the culture to the rules rather than vice-versa. __ Too much focus on logic and stability. __ Seeks to understand how the human mind forms binary opposites. __ Most economic in focus. __ Involves social institutions. • • Psychology Psychology Types of Psychologists For each psychologist, are they clinical, experimental, developmental? Freud: _______ Adler: _______ Jung: _______ Pavlov: _______ Piaget: _______ Skinner: _______ Erikson: _______ Psychology Matching from Handout Name the psychologist associated with each theory. In some cases, name the theory as well. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Children feel inferior so they compensate by looking for experiences that give them a sense of power. This is called ______________________. Personal and collective unconscious. Associate food with bell. This is called __________________. Reward and punishment (or withholding of reward). This is called _______________________. Learning stages take place in the same order and at roughly the same age. Good and bad consequences of actions lead to learning. Identity crisis. Unconscious mind significantly influences behaviour. Psychology • Did you notice any major differences in the way the various psychologists looked at human behaviour? – Were some similar enough to each other that you might classify them into the same school of thought? *Schools of Thought in Psychology • Psychoanalytic Theory = focuses on a view of the mind that includes conscious and unconscious (and its parts). Tends to emphasize unconscious part of mind. • Behaviourism = focuses on what motivates human behaviour, especially through early child-rearing methods. • Learning Theory = focuses on most human behaviour being learned. *See text pages 18-21 for homework. Psychology Matching From Text Name the psychologist associated with each theory. 1. Permissive child-rearing produces well-adjusted children. 2. Strict schedules and rules are good for children while growing up. 3. Kids model behaviour learned through observation. 4. Divided the mind into three parts. They are called ___, ______, ____________. 5. Did experiments with rats, pigeons. 6. Did experiments with dogs. 7. Learning is a result of a stimulus-response effect. Psychology From Text, con’t Neuroses __ A conscience Id __ B anxiety Superego __ C pleasure Ego __ D external reality Food __ E imitation Coloured disk __ F response Bobo the clown __ G stimulus Role Conflict • What are some typical teenage role conflicts? • What are some role conflicts experienced by your parents? Role: Additional Definition • A set of expectations for people who occupy a given social position Deviance: Place the behaviour on the spectrum below • • • • • • • • • • 1: different 3: eccentric 5: offensive 10: illegal Deviance Over Time and Place • Name 3 behaviours that used to be considered deviant in Canadian society but now are not. • Name 3 deviant behaviours that didn’t even exist 20 years ago. • Name 2 behaviours that have different rankings of deviance in different cultures. Therefore, norms… • change over time. • vary from culture to culture, society to society. Sample Quiz Question • Feminist theorists believe that institutions are: A Patriarchal B Equal C Symbolically interactive D clinical TOO SIMPLE A Question • Male dominated is a synonym for: A patriarchy B hierarchy C binary opposite D neurotic