* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monetary and Fiscal Policy Interact
Real bills doctrine wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Helicopter money wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
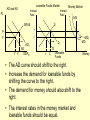
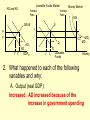
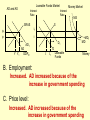
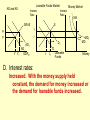
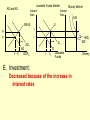
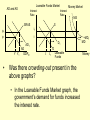
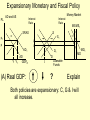
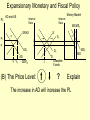
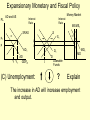
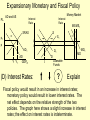
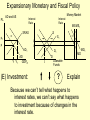
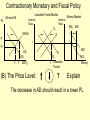
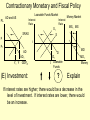
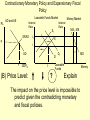
Monetary and Fiscal Policy Interact Unit 5 Lesson 2 Activity 45 By John Morton Advanced Placement Economics Teacher Resource Manual. National Council on Economic Education, New York, N.Y Objectives • Practice analytical skills with AD and SRAS model and the money market. • Analyze the effects of combined monetary and fiscal policies on the loanable funds market. Introduction • This lesson continues an examination of the interaction between monetary and fiscal policy in the short-run. • It examines the impact of monetary and fiscal policy on output, the price level, unemployment, interest rates and investment. • Your success on the AP Exam depends on your ability to explain why economic variables are affected. • Activity 45 provides you with an opportunity to work through the short-run effects of monetary and fiscal policy on important macroeconomic variables. • You will continue to use the loanable funds market and the money market in this activity. (The following slides are not on your activity sheet.) The Effects of Policy Changes in Multiple Markets Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate PL Interest Rate SRAS p Money Market MS S i MD Y AD GDPR D I Loanable Funds Money • Suppose that, in response to the economic situation, the federal government decides to increase its spending without increasing taxes and the Fed keeps the money supply constant. There is no Barro-Ricardo effect. • Explain what would happen in the three markets shown above. Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate PL Money Market Interest Rate SRAS MS S i1 p1 p i D1 AD1 Y Y1 AD GDPR MD1 MD D I I1 Loanable Funds • The AD curve should shift to the right. • Increase the demand for loanable funds by shifting the curve to the right. • The demand for money should also shift to the right. • The interest rates in the money market and loanable funds should be equal. Money Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate SRAS MS S i1 p1 p i D1 AD1 Y Y1 AD GDPR MD1 MD D I I1 Loanable Funds Money 2. What happened to each of the following variables and why: A. Output (real GDP): Increased. AD increased because of the increase in government spending Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate SRAS MS S i1 p1 p i D1 AD1 Y Y1 AD GDPR MD1 MD D I I1 Loanable Funds Money B. Employment: Increased. AD increased because of the increase in government spending C. Price level: Increased. AD increased because of the increase in government spending Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate SRAS MS S i1 p1 p i D1 AD1 Y Y1 AD GDPR MD1 MD D I I1 Loanable Funds Money D. Interest rates: Increased. With the money supply held constant, the demand for money increased or the demand for loanable funds increased. Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate SRAS MS S i1 p1 p i D1 AD1 Y Y1 AD GDPR MD1 MD D I I1 Loanable Funds E. Investment: Decreased because of the increase in interest rates Money Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Interest Rate SRAS MS S i1 p1 p i D1 AD1 Y Y1 • Money Market AD GDPR MD1 MD D I I1 Loanable Funds Was there crowding-out present in the above graphs? • In the Loanable Funds Market graph, the government’s demand for funds increased the interest rate. Money 4. Answer the following questions: A. What could the Fed have done to prevent crowding-out? The Fed could use expansionary monetary policy; thus the government’s demand for funds would not result in an increase in interest rates. A. Are there certain conditions when the Fed should or should not prevent crowding-out? If the economy were experiencing a recession, the Fed would want to prevent crowding-out, but if the economy were at or near full employment and government spending increased, the Fed might not want to prevent crowding-out. Graphing Monetary and Fiscal Policy Interactions • Illustrate the short-run effects for each monetary and fiscal policy combination using AD and AS curves, the money market and the loanable funds market. • Once again, assume that there are no changes in the foreign sector. • Circle the appropriate symbols (↑ for increase, ↓ for decrease, and ? for uncertain), and explain the effect of the policies on real GDP, the price level, unemployment, interest rates and investment. 1. The unemployment rate is 10%, and the CPI is increasing at a 2% rate. The federal government cuts personal income taxes and increase its spending. The Fed buys bonds on the open market. PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Interest Rate SRAS p Money Market MS S i Y AD GDPR MD D I Loanable Funds Money Expansionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Money Market AD and AS Interest Rate Interest Rate SRAS p1 S S1 i1 i p AD1 Y Y1 AD GDPR (A) Real GDP: MS MS1 D1 D MD Loanable Funds I ? Explain Both policies are expansionary: C, G & I will all increase. MD1 Expansionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Money Market AD and AS Interest Rate Interest Rate SRAS p1 S S1 i1 i p AD1 Y Y1 MS MS1 AD GDPR (B) The Price Level: D1 MD D I Loanable Funds ? Explain The increase in AD will increase the PL MD1 Expansionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Money Market AD and AS Interest Rate Interest Rate SRAS p1 S S1 i1 i p AD1 Y Y1 MS MS1 AD GDPR (C) Unemployment: D1 MD D I Loanable Funds ? Explain The increase in AD will increase employment and output. MD1 Expansionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Money Market AD and AS Interest Rate Interest Rate SRAS p1 S S1 i1 i p AD1 Y Y1 MS MS1 AD GDPR (D) Interest Rates: D1 MD D I MD1 Loanable Funds ? Explain Fiscal policy would result in an increase in interest rates; monetary policy would result in lower interest rates. The net effect depends on the relative strength of the two policies. The graph here shows a slight increase in interest rates; the effect on interest rates is indeterminate. Expansionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Money Market AD and AS Interest Rate Interest Rate SRAS p1 S S1 i1 i p AD1 Y Y1 AD GDPR (E) Investment: MS MS1 D1 MD D I Loanable Funds ? Explain Because we can’t tell what happens to interest rates, we can’t say what happens to investment because of changes in the interest rate. MD1 2. The unemployment rate is 6%, and the CPI is increasing at a 9% rate. The federal government raises personal income taxes and cuts spending. The Federal Reserve sells bonds on the open market. PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Interest Rate SRAS p Money Market MS S i MD AD Y GDPR D I Loanable Funds Money Contractionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p MS1 MS S i p1 AD AD1 Y1 Y GDPR (A) Real GDP: MD D D1 I Loanable Funds ? MD1 Money Explain Decreased AD should lower GDP somewhat. AD decreases because of contractionary monetary and fiscal policy. Contractionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p MS1 MS S i p1 AD AD1 Y1 Y GDPR (B) The Price Level: MD D D1 I Loanable Funds ? MD1 Money Explain The decrease in AD should result in a lower PL Contractionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p MS1 MS S i p1 AD AD1 Y1 Y GDPR (C) Unemployment: MD D D1 I Loanable Funds ? MD1 Money Explain Lower output decreases employment on the SRAS curve. Contractionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p MS1 MS S i p1 AD AD1 Y1 Y GDPR (D) Interest rates: MD D D1 I Loanable Funds ? MD1 Money Explain The Fed decreases the money supply, which should result in an increase in interest rates. The increase in taxes and decrease in government spending result in a decrease in interest rates since the demand for loanable funds by the government should decrease. The demand for money decrease because of the decrease I real GDP. Interest rates will be higher if the decrease in demand is less than the decrease in supply in the money market. The interest rate effect is indeterminate. Contractionary Monetary and Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p MS1 MS S i p1 AD AD1 Y1 Y GDPR (E) Investment: MD D D1 I Loanable Funds ? MD1 Money Explain If interest rates are higher; there would be a decrease in the level of investment. If interest rates are lower, there would be an increase. 3. The unemployment rate is 6%, and the CPI is increasing at a 5% rate. The federal government cuts personal income taxes and maintains current spending. The Fed sells bonds on the open market. PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate S Money Market Interest Rate MS SRAS p i AD Y GDPR D I Loanable Funds MD Money Contractionary Monetary Policy and Expansionary Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p i1 MS1 MS S i AD Y GDPR (A) Real GDP: D D1 MD Loanable Funds I ? Money Explain The combined effect on AD is impossible to predict. The fiscal policy is expansionary, and the monetary policy is contractionary. Contractionary Monetary Policy and Expansionary Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p i1 MS1 MS S i AD Y GDPR (B) Price Level: D D1 MD Loanable Funds I ? Explain The impact on the price level is impossible to predict given the contradicting monetary and fiscal policies. Money Contractionary Monetary Policy and Expansionary Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p i1 MS1 MS S i AD Y GDPR (C) Unemployment: D I D1 MD Loanable Funds ? Explain The impact on output and, hence, employment is impossible to predict given the contradicting monetary and fiscal policies. Money Contractionary Monetary Policy and Expansionary Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p i1 MS1 MS S i AD Y GDPR (D) Interest rates: D I D1 MD Loanable Funds ? Money Explain Interest rates will rise because of the increased demand for and reduced supply of loanable funds. Contractionary Monetary Policy and Expansionary Fiscal Policy PL Loanable Funds Market AD and AS Interest Rate Money Market Interest Rate S1 SRAS p i1 MS1 MS S i AD Y GDPR (E) Investment: D I D1 MD Loanable Funds ? Money Explain The increase in interest rates will tend to decrease investments.