* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
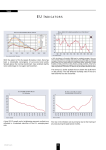
FIN243 – Money and Banking Section 4 Report Group 3 Chan Chun Yeuk 053113 Kwan Yi Ting 053114 Chan Kin Ho 053115 Cheung Tsun Fung 053118 Tam Yiu Hon 053120 Should EEC member countries integrate the currency to be Euro? 1. What is Euro 2. Benefits & drawback 3. Analysis > exchange rate > inflation rate 4. conclusion Robert A. Mundell 1999 Nobel Laureate in Economics What’s Euro? Euro Zone • European System of Central Banks, ESCB • European Central Bank, ECB Duisenberg (First president of the European Central Bank) Trichet (Current president of the European Central Bank) Coins Banknotes All EU member can join • a budget deficit of less than 3% of their GDP • a debt ratio of less than 60% of GDP • inflation and interest rates close to the EU average • • • • • 1/1/2007 - Slovenija 1/1/2008 - Eesti Vabariik, Latvijas, Malta, Cyprus 1/1/2009 - Lithuania, Slovakia 1/1/2010 - Czech Republic, Bulgaria 1/1/2011 – Poland, Hungary, Romania Benefits & drawback The benefits of Euro 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Lower transaction rates Increase trade Transparency & Competition Lower bank reserve Capital Market Low inflation rates Drawbacks of Euro 1. 2. 3. 4. The policies of the members The cooperation of the EEC members Limitation of using Euro External economic factors Analysis 1. exchange rate 2. inflation rate • “Just brings from a simple mind that not to devaluate in currency unit.” • Is that already achieved? • focus on the local effect of Euro • exchange rate and the inflation rate exchange rate variability from 1999 Jan to 2007 Jan. against GBP • purpose of the EMS was therefore to create a zone of monetary and exchange rate stability. • drop in the exchange rate of Euro and there was a trend of being stable after 2003. • Beside the policy factors in Euro in 1999-2002 • people lack of confidence in 2003 • weakness of the US Dollar • between 0.66 and 0.7 exchange rate variability from 1999 Jan to 2007 Jan. against US dollars • same main reason 2002 July • weakness of the US Dollar • could Euro replace the state of the US Dollar • between 1.1 and 1.3, Hong Kong Dollar • linking up with the US Dollar • similar to the US Dollar. 2003 • not drop anymore • already meet its target • to satiable the exchange rate. Inflation rates • Inflation a general rise in prices • Pressure on price adjustment • Asymmetries in the transmission mechanism (Cecchetti, 1999) • demand & supply shock (Bayoumi & Eichengreen, 1993) • • • • New currency not stable Not well developed unpredicted environment factors e.g: exchange rate, oil price. The inflation rate in Euro area and the US • • • • • • • • From the observe : Euro can successful monetary union low inflation rates price stable productive more investment & consumption Export & import Avoiding loss from emancipated inflation • Monetary policy • Lack of degree of freedom to control area – wide inflation • minimizing the deviation of area –wide inflation in long-run • Shrink the inflation rate in Euro &US • Keep the inflation rate in an acceptable level Conclusion • official currency of the Euro zone • process of triangulation BENEFIT DRAWBACK Transaction Costs The policies of the members Increase trade The cooperation of the EEC members Transparency & Competition Limitation of using Euro Fiscal Discipline External economic factors Capital Market Low inflation rates analysis of Euro • Exchange-rate 2003 not drop anymore stable • The Inflation rate keep in the low level no affect the market stable • • • • Euro seems work in some countries Lots of benefits Cannot omit the drawbacks Deep consideration in taking as role model END