* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electricity
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
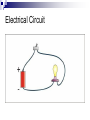
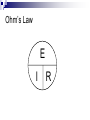
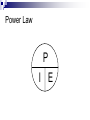
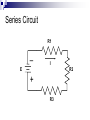
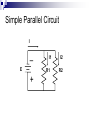
Electricity Residential Construction Parts of An Atom Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus. Protons are positively charged. Opposite charges attract. Electricity occurs when electrons flow from one atom to another. Voltage Voltage is a measure of the Electromotive Force (EMF) in electricity. EMF is the electric force that "pushes" electrons around a circuit. Voltage Measured in volts (v). Algebraic Symbol: E or V Graphic Symbol: ~ _ + Current Current is a measure of the rate of electron flow through a material. Measured in amps (a). Current Algebraic Symbol: I = intensity Graphic Symbol: A Resistance Resistance is the property of matter which opposes the flow of electrons. Measured in ohms (). Resistance Algebraic Symbol: R Graphic Symbol: Conductors Conductors have a large number of loosely attached electrons that can move very easily from one atom to another. Examples: Gold Copper Aluminum Water Insulators Material with a high resistance to electrical current. Electron orbits are very close to the nucleus. Examples: Plastic Rubber Glass Wood Electrical Circuit For electricity to flow, there must be a complete path. Therefore it must have: Conductor (e.g. Copper wire) Energy Source (e.g. Battery) Load (e.g. Light) Control Device (e.g. Switch) Electrical Circuit Ohm’s Law Ohms Law is a mathematical equation explaining the relationship between Voltage, Current, and Resistance. Ohm’s Law The relationship is expressed as E =I*R Where E is Electromotive Force measured in Volts I is Electrical Current measured in Amperes R is Electrical Resistance measured in Ohms Ohm’s Law E I R Calculation Using Ohm's Law equation, calculate Resistance, where: E = 120 volts, I = 15 amps Answer: R = E/I R = 120 v / 15a R =8 Power Power is the ability of electricity to perform work. Measured in watts (W) Algebraic Symbol: P Power Law The relationship is expressed as: P =IxE Where… P is Power measured in Watts. I is Electrical Current measured in Amperes. E is Electromotive Force measured in Volts. Power Law P I E Calculation Using Power equation, calculate Current (I), where: E = 120 volts and P = 800 w Answer: I = P/E I = 800 w / 120 v I = 6.67 amps Types of Circuits Series A Parallel A single path for current to flow. single voltage shared by multiple loads. Complex Combinations of series and parallel circuits. Series Circuit R1 _ I R2 E + R3 Simple Parallel Circuit I _ E I1 R1 + I2 R2 Electrical Tools Wire Strippers/Crimpers Insulated Screwdrivers Electrical Tools Wire sheathing stripper Marrettes / Wire Nuts Electrical Tools Lineman Pliers Needle Nose Pliers Electrical Tools Octagon / Junction Box Switch Box Electrical Tools