* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AC Machines
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
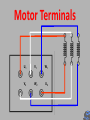
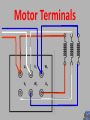
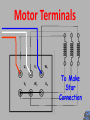
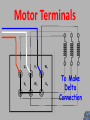
6077SA NUE 046 3 Phase Induction Motor Construction At the end of this section you will be able to: Identify the basic components of a 3Ø induction motor List the types of rotors used Test motor windings for suitability to connect to the supply Connect in both star and delta List the steps for dismantling it 3Ø Induction Motors Why are they so common in industry? Simple in construction Only one moving part Don’t have brush gear and commutators Now with VSD technology, Variable speed Speed of machine fixed to supply frequency Construction Fixed Stator (stationary) Rotor (The bit that Rotates) Construction Frame can be made from cast Iron Steel Aluminium End caps/shields bolted to each end of frame Drip Proof Designed for air flow into motor Not waterproof Not suitable for flame proof atmospheres Totally Enclosed No airflow between motor inside and outside atmosphere Waterproof Easier to adapt to for flame proof atmospheres Open Designed for air flow into motor Not waterproof Very rare due to OH&S considerations Core Laminations Carries the stator windings Made of silicone steel 0.3 to 0.5mm thick Insulated from one another to reduce eddy current loss Stator windings 3 identical phase windings that are displaced by 120° electrical around the stator Each winding consists of series, parallel connected coils to achieve the number of poles required. 2, 4, 6, & 8 poles per phase are common Windings are generally connected in delta but can be connected in star Rotors Wound rotor (not common) Squirrel cage (most common) Two Main Types Squirrel Cage Rotor Squirrel Cage Rotor Can be Cast Rotor bars (slightly skewed) • Aluminium • Copper • Copper alloy End ring Copper/Copper alloy bars inserted into the laminations and welded/brazed to shorting ring Wound Rotor Slip ring Same number of poles as stator. One end of coil is connected to a star point Other end is terminated on a slip ring Resistance is added to change the mechanical and electrical characteristics of motor. Motor Terminals Motor Terminals Motor Terminals U1 V1 W1 V2 W2 U2 Motor Terminals U1 V1 W1 V2 W2 U2 Motor Terminals U1 V2 V1 W2 W1 U2 To Make Star Connection Motor Terminals U1 V2 V1 W2 W1 U2 To Make Delta Connection Electrical Testing Each winding should have the same resistance ie 1-10 Voltage between windings =400V Insulation test level =1000V IR reading no less than 1M