* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motor Vehicle Level 3
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electric vehicle conversion wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Geophysical MASINT wikipedia , lookup
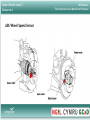
Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Aims To recognize various sensors used within ABS systems and their role within the system Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Objectives By the end of this session you will be able to: •Identify various sensors including hall, and be able to describe passive and inductive sensors and their operation •Recognize the role of the speed sensor and it's location •Recognize and comment on the waveforms produced. •Comment briefly on how to maintain the sensor, and identify possible faults. Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 Types of sensor : Active Sensor •Example:-Magnetised pick up (crankshaft sensor, ABS sensor) •Voltage signal produced is sent to the input of the ECU for analysation. •The ECU will covert this Analogue signal to Digital signal which the ECU can read. •The ECU will now react (alter the brake pressure depending on this voltage signal. ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Types of sensor : Passive Sensor (three wire) •Three wire device •Supply voltage for the sensor is supplied via the ECU •The internal resistance alters with a change in environment these are usually used to sense movement (i.e. throttle position) •This is measured by the ECU and the ECU will alter accordingly Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Types of sensor : Passive Sensor (two wire device) •Similar to a three wire device, the sensors internal resistance will alter with a change in environment rather than change in movement (i.e. engine coolant) •ECU Supplies voltage to the sensor, •The ECU will measure the change in internal resistance and react accordingly. Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors •Of course, ABS will use an active sensor •Why do you think that is? •Could it use a passive sensor? ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced ABS Wheel Speed Sensor •Wheel Speed Sensors are mounted at each wheel and sends a rotation signal to the ECU •Wheel speed sensors can be mounted to the steering knuckle or to the axle carrier Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Wheel Speed Sensor ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Wheel Speed Sensor •As the teeth of the sensor rotor pass the iron core, magnetism will cut through the coil windings Inducing a voltage •When the tooth is centered to the iron core 0v is produced •As the tooth moves away from the iron core, the magnetic field expands producing a negative voltage •As the wheel rotates faster the voltage and frequency increase (indicating to the ECU that the vehicle is travelling faster) ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Waveform produced •In order to diagnose a fault within an ABS system waveforms are useful in order to determine system performance, and will also give hints as to the problem. Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Waveform produced •The following images where taking using a diagnostic tool called a Picoscope •These show two wheel speed sensors being monitored, one has a fault...is it the red trace or the blue trace? Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 Waveform produced ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 Waveform produced •this small capture taken from the waveform produced indicates a fault compared with the blue trace •The fact the we have a waveform at all indicates that the sensor is producing a signal. •Therefore, we can diagnose that the rotor wheel has failed. ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Waveform produced •This vehicle measures rear wheel speed via a driveshaft, upon inspection, we can see that the teeth have been damaged, furthermore, we can see this corresponds to our waveform produced. •Another factor that could have produced a similar waveform could have been distance from the sensor to the rotor or contamination of the sensor. Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 Waveform produced •In order to check the voltage is correct to the sensor •Ensure that your multimeter is correct and on the correct function (direct v) •Measure between the terminals as shown (always refer to manufactures guidelines) •The voltage should be between 10v-14v ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 Probing a Sensor •Continuity check •Is done to check that there is no faults in the wiring harness between the ECU, the Actuator and the ABS relays and possibly to the sensors. •Refer to manufactures guidelines •From the signal contact in the terminal blocks check the resistance between each components. •The resistance should be around 4-6Ώ ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Motor Vehicle Level 3 Resource 4 ABS Sensors Their Operation and Waveform Produced Summary Have We:•Identified various sensors including hall, and be able to describe passive and inductive sensors and their operation •Recognized the role of the speed sensor and it's location •Recognized and commented on the waveforms produced. •Commented briefly on how to maintain the sensor, and identify possible faults.