* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download rectification - El Camino College
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Vacuum tube wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
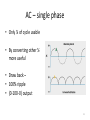
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
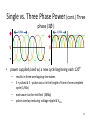
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
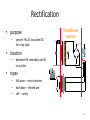
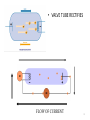
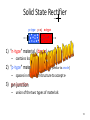
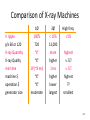
RECTIFICATION RT 244 – Lect #2 Rev 2012 1 Wavelength • X-ray is measured • In HERTZ OR • Angstrom XRAY IS MEASURED IN HERTX OR ANGT Elsevier items and derived items © 2009 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 2 Alternating Current - AC • AC is produced when a coil of wire turns in a magnetic field • ½ turn current is moving in one direction • Then ½ turn it moves in the other direction • IF 3 coils of wire are wrapped around a core – they rotate 1/3 (120º apart) – then 3 different AC currents are generated 3 Rectification • • • • • Converts AC to DC Located after Step up Transformer On secondary side of Circuit Can be single phase (1Φ) Or 3 phase (3 Φ ) 4 Rectification • process of changing AC to pulsed DC • rectifier – device that allows I to flow in only one direction – types valve tube solid state + Ie I + - I Ie 5 Rectification • purpose – convert HV AC to pulsed DC for x-ray tube Transformer Section • location – between HV secondary coil & x-ray tube • types – – – full wave -- most common half wave -- limited use self -- rarely 6 Valve tube (diode) glass vacuum tube w/ 2 electrodes anode cathode cold hot 1) negative electrode -- cathode – thermionic emission of e- 2) positive electrode -- anode – cold metallic plate 7 • VALVE TUBE RECTIFIES FLOW OF CURRENT 8 SOLID STATE - DIODES – Semi Conductor • Allows current to only flow in one direction • Most common type used in rectifiers 9 Solid State Rectifier p-type p-nj n-type - - -- - - - -- - 1) "n-type" material (donor) [similar to cathode] – contains loosely bound e- 2) "p-type" material (acceptor) [similar to anode] – spaces in molecular structure to accept e- 3) p-n junction – union of the two types of materials 10 TYPES OF RECTIFICATION SINGLE PHASE ½ RECTIFIED + FULL RECTIFIED 11 Rectification Process • rectifiers placed in circuit to convert AC current to pulsed DC • methods – suppress unwanted part of the AC + V - + I - – redirect unwanted part of AC + V - (half wave rectification) (full wave rectification) + I 12 AC – single phase • Only ½ of cycle usable • By converting other ½ more useful • Draw back – • 100% ripple • (0-100-0) output 13 Single Phase – Full rectifiedVoltage +V +V 0 0 -V -V • 1Ø AC has a 100% voltage ripple 14 Single vs. Three Phase Power (cont.) Three + 1/60s • phase (3Ø ) 1/60s + V V - - power supplied/used w/ a new cycle beginning each 120° – – – – results in three overlapping sine waves 3 + pulses & 3 - pulses occur in the length of time of one complete cycle (1/60s) each wave can be rectified (3Ø6p) pulses overlap reducing voltage ripple & Vmin 15 3 PHASE – MORE EFFICIENT 16 3Ø comparison to 1Ø • 3Ø more efficient than 1Ø • 3Ø requires more complex circuitry • 3Ø more expensive to install 17 (3 Φ ) 3 PHASE • LESS RIPPLE • MORE EFFIECIENT OUTPUT • HIGH FREQUENCY – 1% RIPPLE • MOST EFFIEICENT – VERY EXPENSIVE 18 VOLTAGE RIPPLE • 100 % RIPPLE • 4 – 10 % RIPPLE • 1% RIPPLE Ripple effect differences 19 Voltage Waveforms (Bushong) Single phase Rectification Type Ripple Half wave 100% Full wave 100% Rectified 3-phase Rectification Type Ripple Three phase, 6 pulse 13% Three phase, 12 pulse 4% Three phase, high frequency <1% 20 Generator Summary Type 1ØSelf p/c 1 p/s 60 # rectifiers 0 % Ripple 100% Wave Form (2 cycles) + + 1Ø1p 1 60 1 or 2 100% - 1Ø2p 2 120 4 100% + - 3Ø6p 6 360 6 or 12 + 12-15% - 3Ø12p 12 720 12 3-5% + - 21 Comparison of X-ray Machines 1Ø 100% 720 “X” 3Ø < 15% 13,000 more High freq. <1% X-ray Quality min time machine $ “X” 1P (~8 ms) “X” higher 1 ms higher highest operation $ generator size “X” moderate lower largest ?? smallest V ripple p/s 60 or 120 X-ray Quantity highest 22 Ripple Factor (%) • variation in tube V during an exposure • What is the ripple of the following waveform? 80 kV 68 kV + V - 1/60s = look in book for comparisons 23 High Frequency Generators rectifiers smooth chopped HV T rectifiers smooth tube • x-ray tube nearly constant – ripple <1% • small in size • Expensive – most efficient 24 Full-Wave Rectification + I - Positive HV pulse + + - + V - Negative HV pulse - - x rays + + Ie x rays Ie + I - I + V - FYI - Don’t need to know the direction of the current I + I - 25 High Frequency Power • machine designed to have a low ripple (<1%) & use 1Ø power • 1Ø AC rectified then smoothed & chopped into high frequency output (kHz) 26 1Ø vs. 3Ø HV Transformers Each phase must have step-up transformer 3Ø 1Ø primary secondary primary secondary 27 3 Transformer Configurations simple 3 6 pulse: delta/wye (DU) primary secondary 15% voltage ripple Star Wye or delta 28 3 Trans. Configurations (cont.) complex 3 6 pulse: delta/wye/wye (DUU) primary secondary 12% voltage ripple 29 3Ø Transformer Coils Delta Coils Wye Coils Wye -- delayed output Delta -- either side Wye -- secondary only + 1/60s V - 30 3 Rectification • each secondary coil requires 2 rectifiers • 3Ø6 with DU coils = 6 rectifiers positive pulse negative pulse - + + - + + - 31 3 Rectification (cont.) • 3Ø6 with DUU coils = 12 rectifiers positive pulse + + negative pulse + + + + - - 32 3 Rectification (cont.) • 3Ø12 with DUD coils = 12 rectifiers positive pulse + + negative pulse + + - + - + - 33 A star or delta connection is used to ? 34 3 Transformer Configurations simple 3 6 pulse: delta/wye (DU) primary secondary 15% voltage ripple A star or delta connection is used to combine three-phase current 35 Rectification • D AC to DC • Keeps e- flowing from cathode to anode • Uses rectifying bridge between HVT & tube tube HVT AC bridge DC tube HVT 36 Capacitor Discharge Generator HV T • • • rectifiers capacitor tube capacitor bank charged by rectified high voltage during exposure capacitors provide kV across tube problems – as capacitors drain kV drops (~1 kV/mAs) – any residual charge may shock operator PLUG IN PORTABLE MACINES 37 TECHNIQUE CHANGES • SINGLE PHASE (1Φ) TO • 3 Φ 12 PULSE CUT MAS BY ½ • SINGLE PHASE (1Φ) TO • 3 Φ 6 PULSE CUT MAS BY 1/3 MORE EFFICIENT = LESS MAS NEEDED 38