* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Handout Topic 11.2 questions solutions 2015
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Optical rectenna wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
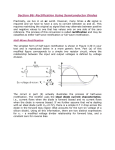
Handout Topic 11.2 HL Only – Basic Questions Rectifying AC I. Half Wave Rectification 1. Why do you need a diode in a rectified current? Because, by definition, a rectified circuit converts AC to DC. A diode only allows current to flow in one direction + - which is the fundamental idea of direct current. 2. a) What does the symbol of the diode represent and what is the anode and cathode? An arrow indicating one direction of current ( DC). Anode = + Cathode = b) In standard sign convention a circuit always follows which charge? Positive 3. Summarize half – wave rectification using the following words in your explanation: forward biased, reverse biased, transformer, diode, half cycle and load resistor. In review : The transformer transforms or “ rectifies” AC to DC and relays it to the diode. Diode is “ON “ ( forward biased) provides rectified current = dc current supplies rest of the circuit ( load resistor) with direct current. Remember that the load resistor is just the part of the circuit – could be a fan, light or anything, that receives the “ rectified current” i.e direct current ( dc) when the diode is “ON” i.e. forward biased….lots of vocab! 4. Draw an label a graph of potential difference vs. time showing the half-wave rectification cycle. II. Full wave rectification 5. What is the fundamental difference between half wave and full wave rectification? Half wave rectification causes ripple where the voltage ( pd) is not constant. Full wave rectification allows more control over V output by using a full cycle-wave control of the voltage output. 6. Compare full wave rectification to half wave rectification in terms of diodes. Full wave rectification uses two diodes instead of only one as in half wave rectification. The two diodes are able to alternate between off and on depending on the direction of the DC current. In this way , with the two diodes, you can control the V ( pd) output through out the entire cycle and avoid the ripple effect thereby maintaining a constant, steady supply of DC current and V output.