* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Do now! - MrSimonPorter
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Protective relay wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
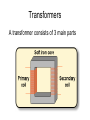
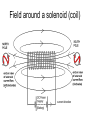
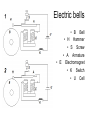
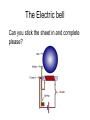
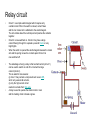
Do now! Can you stick the sheet in your book please? Last lesson - Transformers Transformers A transformer consists of 3 main parts Transformers A changing current in the primary coil produces a changing magnetic field in the core. This changing magnetic field induces a changing current in the secondary coil. Changing voltages The ratio of the number of turns on the coils equals the ratio of the voltages # of turns = Np # of turns = Ns Vp/Vs = Np/Ns Changing voltages A transformer where the voltage rises is called a step-up transformer Changing voltages A transformer where the voltage falls is called a step-down transformer No energy for nothing However, no new energy is made No energy for nothing Power in = power out VpIp = VsIs a.c. only Because transformers rely on induction (changing fields), they only work with alternating current (a.c.) Why do we need transformers? Why do we need transformers? Current flowing through wires causes them to get hot and energy is lost. Why do we need transformers? Keeping the current low means electricity can be transported long distances without losing too much energy. Why do we need transformers? However, in order to send a large quantity of energy, high voltages are needed. Transmission of Electricity Step-up Step-down Today’s lesson • • • • • Field around a wire Field around a coil (solenoid) Electromagnets Bells Relays Can you gather around Mr Porter? Moving charges (currents) Moving charges (electric currents) also produce a magnetic field Conventional current – electrons flow in the opposite direction http://www.sciencebuddies.org Magnetic field around a straight wire You can use the right hand screw rule to decide which direction the field goes Stronger field closer to wire Magnetic field around a straight wire You can use the right hand screw rule to decide which direction the field goes Stronger field closer to wire Can you copy this? Shape around a coil (solenoid) Can you gather around Mr Porter? Field around a solenoid (coil) Electromagnets To make an electromagnet stronger? To make an electromagnet stronger The 3 C’s • More Coils • More Current • Use an iron Core Can you copy this? Electric bells • Can you gat Electric bells • B Bell • H Hammer • S Screw • A Armature • E Electromagnet • K Switch • U Cell The Electric bell Can you stick the sheet in and complete please? Relays Relay circuit Relay circuit • • • • • Circuit 1 is a simple electromagnet which requires only a small current. When the switch is closed, current flows and the iron rocker arm is attracted to the electromagnet. The arm rotates about the central pivot and pushes the contacts together. Circuit 2 is now switched on. Circuit 2 may have a large current flowing through it to operate a powerful motor or very bright lights. When the switch is opened the electromagnet releases the rocker arm and the spring moves the contacts apart. Circuit 2 is now switched off. The advantage of using a relay is that a small current (circuit 1) can be used to switch on and off a circuit with a large current (circuit 2). This is useful for two reasons: (i) circuit 1 may contain a component such as an LDR, which only uses small currents, (ii) only the high current circuit needs to be made from thick wire. A relay is used to operate the starter motor in cars and the heating circuit in diesel engines.