* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Charging System Fundamentals
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
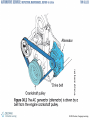
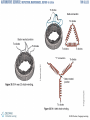
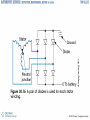
Charging System Fundamentals Chapter 30 © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Objectives • Explain electrical generation principles • Describe AC generator parts • Explain the operation of a voltage regulator © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Introduction • Charging system – Important part of electrical system – Allows battery to maintain charge and operate accessories © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Charging System • Charging system components – Alternator and voltage regulator – Dash light or gauge – Related wiring • Charging replenishes the battery – Output increased when load causes battery voltage to drop • Starter motor is a large load on the battery – AC generator recharges battery and supplies electrical needs © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Direct Current (DC) Generators • Older cars used DC generators – Produces AC • Output is DC because its commutator has brushes on north and south poles • Drawbacks – – – – More current must flow through brushes Brushes wear out Speed limited to 10,000 rpm Do not produce enough output at slow speeds to supply electrical accessories © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning AC Generator/Alternator • Alternator is an AC generator – Electromagnet passes across wire to induce voltage • Stator: stationary conductor • Rotor: rotating electromagnetic field © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Rotor Construction • Rotor: magnetic field that rotates within the stator’s wire windings – Very little clearance to maintain strong field – Field coil has electrical wire wound around a shaft – Poles fit into each other • Make several pairs of north and south poles • Increases magnetic flux – Average rotor can spin at about 13,500 rpm © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Stator Windings • Three sets of windings wrapped around slots in laminated round iron frame (i.e., core) – Each winding has two leads: one for current to enter and one to exit © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Rectifier Construction • Diode rectifier converts AC to DC – – – – When AC current reverses, the diode blocks A pair of diodes is used for each stator winding Three positive diodes are mounted in a heat sink Three negative diodes mounted in the alternator frame • Three phases of AC are rectified – Result is almost uniform DC voltage © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning AC Generator Bearings • Rotor is supported in alternator housing using ball or roller bearings – Bearings are usually sealed and packed with grease – Front bearing fits into indent in the case – Rear bearing is pressed-fit into the case – Rotor shaft slides into rear bearing • AC generator fan – Cooling fan draws air into AC generator © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Voltage Regulator • Controls current passing through windings of electromagnetic field in the rotor – Determines amount of current produced in stator – Increases current output when charging system voltage is low • Electronic voltage regulators – No moving parts or contacts: very reliable – Zener diode conducts electricity when a certain voltage is reached © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Voltage Regulator (cont'd.) • Computer voltage regulation/pulse – Voltage regulation on late-model vehicles is done by the on-board computer, or powertrain control module – Electronic voltage regulation: can cycle 10-7,000 times per second – Pulse width modulation: turning alternator on and off rapidly © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning Charging System Indicators • Charge indicators – Warning light – Voltmeter – Ammeter • AC generator warning light – Wired into charging circuit • Voltmeter indicator – Shows system voltage when engine is running • Ammeter indicator – Gives current amount flowing to or from battery © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning High-Voltage Charging Systems • Important dates and concepts – 1970: automobile required about 500 watts – 2008: vehicle requires about 4,000 watts – 2020: BAS systems will be included on all internal combustion engine vehicles • BAS systems use 42-volt electrical systems with a 36-volt battery pack • BAS motor/generator: larger than conventional AC generator © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning High-Voltage Charging Systems (cont'd.) • Hybrid vehicles – More electrically powered components – Use a generator with inverter/converter • Converts battery pack voltage to low voltage to power the computer and accessories © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning