* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
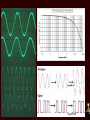
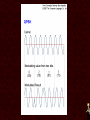
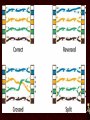
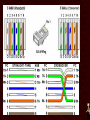
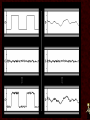
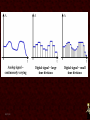
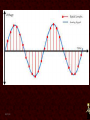
Networking Fundamentals •Copper Core Cable as Network Media • Medium: Copper Signals Analog and Digital Signals • Frequency - repeating event per unit time Hz or Hertz – cycles per second • • Attenuation - A gradual loss of any kind through a medium • Interference - • Latency - the combination of two or more electromagnetic waveforms to form a resultant wave a measure of time delay experienced in a system • Medium Copper Data Transmission Data Transmission • Bandwidth – (1) width of the range (or band) of frequencies that an electronic signal uses on a given transmission medium (usually in hertz, hz) (2) data transfer rate (usually in bits per second, bps) • Baseband - • Broadband - multiple signals and traffic types a single unmultiplexed signal Data Transmission • Simplex – one way • Duplex – two way Full-Duplex – all the time Half Duplex – one at a time Signal Encoding, Digitization • • • • • Frequency Shift Keying - FSK Amplitude Shift Keying - ASK Phase Shift Keying - PSK QPSK QAM64 8/25/13 • Medium Copper Important Electronic Terms Electronic Terms • Direct Current the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by sources such as batteries. • Alternating Current the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. Electronic Terms • Resistance (DC) the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that conductor. • Impedance (AC) the opposition that a circuit presents to a current when a voltage is applied. Electronic Terms • Reflected Loss the loss of signal power resulting from the reflection caused at a discontinuity. • Crosstalk phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Electronic Terms • Induction a redistribution of electrical charge in an object, caused by the influence of nearby charges. • Decibel A unit used to express relative difference in power or intensity, usually between two acoustic or electric signals, equal to ten times the common logarithm of the ratio of the two levels Crosstalk • • • • Near-End Far-End Equal Level Far-End Alien Crosstalk • Medium Copper Copper Core Cables Copper Core Cables • Coaxial Cable • Twisted Pair • Medium Copper IEEE 802.3 - Ethernet IEEE 802 • 802 Network Standard .1 Internetworking .2 Logical Link Control .3 Ethernet over copper cabling .11 Wireless http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802 IEEE 802.3 Standard (1000+pages) • Classifications 10BaseT 100BaseTX 1000BaseT 10GBaseT • 10 Mbps 100 Mbps 1000 Mbps 10 Gbps Baseband Baseband Baseband Baseband Twisted Pair (Cat5) Twisted Pair (Cat5) Twisted Pair (Cat5e) Twisted Pair (Cat6) Media Access CSMA/CD carrier sense multiple access with collision detection • Wiring and Connections 568A 568B RJ-45 Connector Straight-Through (Patch) Crossover Auto-MDIX – Automatic Medium-Dependent Interface Crossover • Medium Copper IEEE 802.5 IEEE 802.5 Standard • 802.5 Token Ring • MAU – Multiple Access Unit • Medium Copper Wiring Faults Wiring Faults • Short – Bad connection • Open – Break in connection • Ground – Connects to Earth • Reversed – Reversed Pair • Crossed – Crossed pair • Split Pairs – Split Pair • Medium Copper Etc. Etc • Etc 8/25/13 8/25/13 8/25/13 8/25/13 8/25/13 8/25/13 8/25/13 8/25/13 8/25/13