* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Property Classification through Sensing MIDN 1/C Nicholas
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Lego Mindstorms wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Beams wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Signal Corps (United States Army) wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
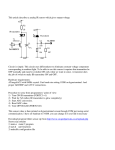
Property Classification through Sensing Capacitive Sensor Setup Rabbit 2000 MIDN 1/C Nicholas A. Dadds Advisor: Dr. Svetlana Avramov-Zamurovic Co-Advisor: Dr. Kenneth A. Knowles Weapons and Systems Engineering IC Cable Temperature Sensor Stanton 400.V3 Signal Conditioning Circuit Stylus MLX90247 Sensor Roughness Sensor Left GND Left Signal Aluminum Roughness Profile 5V 47k V oscope Material AD7746 *Converts capacitive reading to digital info for Rabbit* Capacitive Sensor Leads PVC Roughness Profile *Output signal is an analog voltage C d const. Lead Length Dielectric constant of Material Material Type Classification Based on Capacitance Material Mean Relative Capacitance Uncertainty [% Full [ppm] Scale] Air 0.59597 7 Wood 0.59931 7 PVC 0.59705 7 Aluminum 0.5732 50 * In order to avoid contact between the Aluminum material and the sensor a sheet of paper was placed in between the two for isolation* Signal Conditioning Circuit Internal Schematics The dielectric constant in the capacitance equation above varies depending on the type of material placed around the sensor. Therefore, each specific material type will produce a unique capacitive result. Under stable conditions, when calibrated for a specific set of materials this sensor is capable of providing data useful in determining what material is in the surrounding environment. The plots shown above were obtained through the use of the Stanton 400.V3 Stylus. These plots show the general surface roughness of a given material and when viewed in comparison we get an idea of how the two surfaces relate to each other with respect to their roughness characteristics. We are able to compare the mean voltage value produced across a defined length of the material as well as the maximum peak voltage value, and the frequency of occurrence. Currently the roughness sensor is only connected so that it can obtain signals when moving to the left. However, for future work we will connect the right signal as well as design a device that will standardize the height and displacement of the sensor for each measurement. Wood Roughness Profile Signal Conditioning Circuit Roughness Sensor Stylus Left GND Left Signal Stanton 400.V3 5V 47k V oscope PVC Roughness Profile Aluminum Roughness Profile Wood Roughness Profile