* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
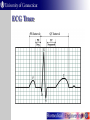
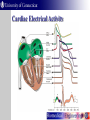
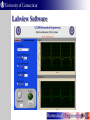
Vital Signs Monitor UConn BME 4900 Vital Signs Monitor Purpose As the population ages, many people are required by their doctors to take vital signs on a daily basis. Developed for the average person to use at home. Vital signs transmitted to a computer and ultimately to a doctor. Measurements What can it measure? Electrocardiogram (ECG) Three leads (Right arm, left arm, right leg) Respiration Thermistor Body Temperature NTC Thermocouple What is an ECG? Records a time waveform of heart electrical activity. Used to diagnose heart problems Arrhythmia Myocardial infarction Conduction blocks (bundle branch block) ECG Trace Cardiac Electrical Activity The ECG Waveform Measuring Electrical Activity 3 leads 2 arm 1 leg As cardiac muscle depolarizes it creates a potential on the skin Potential measured as a vector Difference between right and left electrode measured with a differential amplifier. Measuring Electrical Activity Circuit consists of: 3 op amp differential amplifier Low pass filter (Cutoff: 0.05 Hz) High pass filter (Cutoff: 160 Hz) Gain Amplifier Differential Amplifier Feedback Amplifier Buffer What does the buffer do? Provides a high input impedance What is the purpose of C2 and C3? Remove DC offset Why? Offset would be amplified by 1000x 10 mV at 1000x gain = ~10V Differential Amplifier Differential Amplifier V1 & V2 are in the microvolt range We need it to be in the milivolt range so Rf/R1 is set to ~1,000 1st Order LPF The ECG is known to be a low frequency signal A LPF can be used to remove the high frequency noise in the signal High Pass Filter ECG frequency range ~0.05 Hz – 150 Hz Why do we need to eliminate frequencies <0.05 Hz? Avoid distortion of the ST wave Respiration Measured with thermocouple placed in nostril During exhalation warm air passes through nose During inhalation cooler air is drawn in Respiration What is a thermocouple? Two different metals joined together Temperature changes induce a voltage Voltage can be linearized to temperature Respiration Non-inverting amplifier Gain = (1 + R2 / R1) Multiplies thermocouple voltage by gain R2 R1 Body Temperature Often indicates infection “Normal” temperature – 98.6ºF (37ºC) Measured with negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor Resistance decreases as temp. increases Body Temperature Wheatstone Bridge Rx = Thermistor R1, R2, R3 = 4.7k Ohm Differential amplifier Body Temperature Waveform Voltage decreases over time Time shown at right ~90 seconds Voltage at steady-state can be converted to a temperature measurement Microprocessor Provides Analog to Digital (A/D) conversion Waveform y(t) sampled at a fixed rate Δt Voltage read every Δt and converted to a number If resolution is 8 bits 8 Gives us 2 = 256 counts over 5V range ~19.5 mV per count Digital Isolator Isolates the patient from the computer Receives data from microprocessor Uses Giant Magnetoresistance for isolation Digital pulse induces a magnetic field across an isolated barrier RS232 Converter Input from isolator Converts 5 V UART signal from microprocessor to RS-232 standard RS-232 standard +10 V – 10 V digital signal Switching Between Signals Three signals that can be measured Only one is recorded at a time A mode switch is used to select which signal is processed When a mode is selected a flag is sent over the serial port Flag indicates which mode Labview reads flag and changes modes Labview Software Labview Requirements Receive serial data from microprocessor Read mode flag and switch to appropriate screen Display EKG, and Respiration waveforms Calculate respiration rate (number of peaks / time) Read voltage from thermometer and convert to body temperature