* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
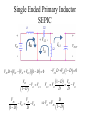
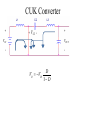
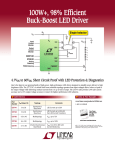
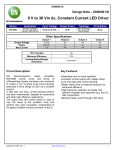
Topology Impacts on Component Stress + Vo Vd + - - Parameter Transistor Vˆ Transistor Iˆ - Buck Vin I out - Boost Vin Vout I in Iin I out DI in Transistor I DI out DI in Diode I 1 D Iout Pulse Current Input Buck/Boost Vout DI out I out - - Transistor I rms Inductor I + Vo Vd + + Vo Vd + 1 D Iin I in Output D I in I out D I in I out 1 D I in Iin I out Both I out Single Ended Primary Inductor SEPIC + VIN + IL1 VC2 + - IL3 IL3 - VOUT - VIN D VIN VO VC 2 1 D 0 VIN VO VC 2 1 D VIN VO VO VO D 1 D VC 2 D VO 1 D 0 VC 2 VO 1 D D D VO VIN 1 D VO VO D CUK Converter + + VC2 - VIN + VOUT - - D VO VIN 1 D Worst Case Conditions If it is desired that a converter operate in CCM at all times, it must be recognized that DCM occurs for low values of inductor currents. For regulated output applications, this condition is associated with large resistance (low current) loading, and/or high input voltages. Inductor values should be chosen accordingly, with appropriate safety factors. Low Voltage Applications For low output voltage applications (~ 1 v) the voltage drop associated with a freewheeling diode may be unacceptably high. In this case, the diode is replace by another active switching device with very low ON-resistance. Interleaving Converters Multiple converters can be operated in parallel with their switching waveforms delayed with respect to each other (phase shifted). This tends to smooth out the residual pulsation currents.