* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surface-conduction electron-emitter display wikipedia , lookup
Stereo display wikipedia , lookup
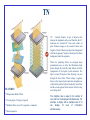
LCD TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW C O N T E N T S: TN STN FSTN DOUBLE STN ECB COLOR (F)STN MULTI-COLOR TN SURFACE MOUNT TECHNOLOGY CHIP-ON-BOARD CHIP-ON-GLASS TAPE AUTOMATED BONDING BACKLIGHTING INTERFACE TEMPERATURE RANGES Tianma Microelectronics (USA) Inc. TN TN – Twisted Nematic. A type of liquid crystal whereas the alignment surface and therefore the LC molecules are oriented 90° from each surface of glass. Produces images in two modes: Positive and Negative. Positive Mode provides white background with black segments. Negative Mode provides black background and white segments. FEATURES * Backgrounds: Black, White * Viewing Angle: 45 degrees (typical) * Multiplex Ratio: up to 64:1 (segments / commons) * Most inexpensive When two polarizing filters are arranged along perpendicular axes, as in the first illustration, light passes through the lead filter and follows the helix arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules. The light is twisted 90 degrees, thus allowing it to pass through the lower filter. When voltage is applied, however, the liquid crystal molecules straighten out of their helix pattern. Light is blocked by lower filter and the screen appears black because of there being no twisting effect. The multiplex rate is equal to the number of rows that can be displayed simultaneously. For example, a display with a multiplex rate of 16 can display 16 rows of information simultaneously. STN STN – Super Twisted Nematic. A high information content LCD that uses adjustable interference of two optical modes to achieve a large number of multiplexed lines, higher contrast and higher level of gray scale. It results in the birefringence mode. An improved twisted nematic fluid (200° twist or greater) which has better contrast and optimum viewing range than standard twisted nematic. The graph shows a comparison of a voltage versus transmitted light curve of a typical TN and a supertwist nematic (STN) display. (Generally, a greater twist angle equates to higher multiplexibility.) The V90 and V10 points on the graph indicate the voltages that yield 90 percent and 10 percent light transmission, respectively. FEATURES * Backgrounds: Yellow-Green, Gray, Blue * Viewing Angle: 75 (typical), 90 (maximum) degrees * Multiplex Ratio: up to 480:1 (segments / commons) * Response Time: 150 msec (lower than TN) * Suitable for Graphic applications As the figure shows, STN displays have a steeper curve than TN displays, which allows higher multiplex levels for STN displays. (STNs were developed primarily to overcome the difficulties encountered in multiplexing TN displays.) The multiplex rate is equal to the number of rows that can be displayed simultaneously. For example, a display with a multiplex rate of 400 can display 400 rows of information simultaneously. FSTN FSTN – Film Compensation Super Twisted Nematic. LCD with an extra film added to the outside of the cell to compensate the color shift of blue on green to black on white. The film is made of a polymer with double refraction to remove the interference of colors. It results in retardation compensation. The film (the top layer in the figure) is placed in the display, either under or over the top polarizer. Some film compensation systems use two films, one on the rear that serves as a collimator, and one on the front that serves as a dispersion film to broaden the viewing cone. Film compensation improves the viewing angle, but does not affect switching time. FSTN is all standard STN displays with a polymer film applied to the glass as a compensation layer instead of the second cell as in the case of the DSTN. This simpler and more importantly cost effective method provides the preferred black on white image for this display technology. FEATURES * Backgrounds: Black, White * Viewing Angle: 80 degrees (typical) * Multiplex Ratio: up to 480:1 (segments / commons) * Response Time: 150 msec (lower than TN) DSTN DSTN, developed by Sharp Corporation, was the first commercial black and white conversion of the STN display and refers to Double Super Twisted Nematic. DSTN displays are actually two distinct STN filled glass cells glued together. The first is a LCD display, the second is a glass cell without electrodes or polarizers filled with LC material for use as a compensator which increases contrast and gives the black on white appearance. There are only a few manufacturers that offer this technology: Tianma, Optrex, Hyundai, URT, Varitronix and CFG. Here is an overview of DSTN technology by different criteria: Contrast: better than STN, FSTN; offers automatic contrast compensation with temperature. Response Time: significantly enhanced. Optical Cast: DSTN reduces the tendency of a screen to be slightly red, green or blue. Viewing Angle: combination of 6 and 12 o’clock optimal viewing directions together Temperature Range: -30 to +80 C operating, -40 to +90 C storage Polarizer Mode: Negative, so DSTN LCD’s need backlighting Back Light: CCFL or LED only Resolution: up to 122 x 32 dots Suitable Applications: Automobiles, Gasoline Pumps, etc. Always custom designed ECB Features of ECB Color LCD Modules: Low power consumption – Under most lighting conditions, no backlight is required which saves the highest power-consuming element of the display. Simple drive electronics – The single pixel for all four colors requires only one set on common and segment drivers. This also reduces the connector pitch, the cost, and complexity of the assembly. No color filters – Reflective operation is possible in most environments. Color filters add cost and require a backlight to provide enough illumination to overcome the loss of a given pixel. Low cost – The reduced electronics and lack of filters make the module significantly lower in cost comparatively with passive color STN modules. Response Time: about 250 msec (low) Low Transmission: about 1.5 to 20 % Applications: Gaming, etc. Being very sensitive to extreme temperatures and responsively slow, ECB technology is not suitable for the automotive industry or video applications. Always custom designed. Electronically Controlled Birefringence (ECB) or Vertically Aligned Nematic (VAN) is a electro-optical effect that was first described in 1971. Through this effect a number of distinct colors can be displayed in a LCD. The ECB mode color displays are realized by controlling both the birefringence of liquid crystals and a pair of optimizing polarizers with retardation films, which are brought from operating voltage rate impressed to liquid crystal layer and inclination of liquid crystal molecules. Thus, the wavelength of light exciting a pixel is determined by the voltage applied to that pixel. Almost every other LCD manufacturer offers this technology today. TYPES OF ECB PRODUCT STN: multiple colors on green background FSTN: multiple colors on pale background MULTI-COLOR TN Advantages: •Allows a limited number of colors that are not subjected to change •Less parallax and durability problems compared to most conventional designs available on the market •Resistant to wide range temperatures (-30 to +80 C operating ) •Inexpensive (TN technology has become conventional almost 30 years ago) • Applications: high quality audio and car displays, etc. The newly developed Selective Multi-Color TN LCD technology is offered only by Tianma, Optrex, and Varitronix. Multi-Color TN display is based on the negative mode. The color coatings and the black matrix (mask) are inside the LCD cell. The black mask allows the light go through characters and icons only, not the background. The total number of colors ranges from one to three in addition to the black matrix. Customers can select the color for each segment. No bleaching of colors is observed even when operating at 80 C, ideal for automotive and other outdoor applications. Displays from static to 1/8 multiplex are available. Black mask is used to mask off non- switching areas in alpha-numeric segment displays. The purpose is to improve contrast and readability. This way, a stronger backlight can be used. IC MOUNTING TECHNOLOGIES IC COMPARISON Tianma Microelectronics implements a variety of integrated circuit mounting methods in designs of printed circuit boards used with standard and custom made liquid crystal modules. Tianma has full production capabilities that incorporate design requirements for the following IC mounting technologies: Surface Mounting Technology (SMT) Tape Automated Bonding (TAB) Chip-On-Board (COB) Chip-On-Glass (COG) During the days of high demand of integrated circuit components on the LCD market, Tianma Microelectronics manages to keep firm control of receiving IC supplies from contractors. Despite the shortage of micro-controllers and drivers in the LCD industry, it is entirely within Tianma Microelectronics’ capabilities to provide its customers with large quantities of high quality electronic chips supporting the present product line. SURFACE MOUNT TECHNOLOGY (SMT) QUAD FLAT PACKAGE Surface Mounting Technology (SMT) using quad flat packages on printed circuit boards was the most popular at the early years of liquid crystal display industry, and is still available for mass production. Plastic Quad Flat Package (QFP) represents itself as a flat rectangular integrated circuit package with its leads projecting from all four sides of the package without radius. Used with surface mounting method. Made of black epoxy resin. Very moisture absorbent. CHIP-ON-BOARD (COB) BARE DIE Chip-on-Board (COB) is a popular IC mounting method that provides wire bonding as the direct attachment of bare die to laminated printed circuit boards. The LCD driver is formatted into an area on the PCB. Electrical connections are made by micro diameter gold wires. The entire area is then covered with epoxy. All of Tianma’s standard Character LCD modules are of the Chip-On-Board design. Advantages: • Very compact • Space savings over Surface Mount Technology assembly. • Cost savvy comparatively with SMT, since there is no plastic package. CHIP-ON-GLASS (COG) Chip-On-Glass – is one of the high-tech mounting methods that uses Gold Bump or Flip Chip IC’s, and implemented in most compact applications. Chip-On-Glass integrated circuits were first introduced by Epson. In flip-chip mounting, the IC chip is not packaged but is mounted directly onto the PCB as a bare chip. Because there is no package, the mounted footprint of the IC can be minimized, along with the required size of the PCB. This technology reduces a mounting area and is better suited to handling high-speed or high-frequency signals. Currently, there are 3 standard C.O.G. LCD modules available at Tianma with the regular mass production delivery time. Advantages: 1. Very space economical. Chip-On-Glass LCD modules can be as thin as 2 mm. 2. Cost effective over COB, especially in graphic LCD modules, because much less IC's are required. 3. More reliable than TAB because of the weakness in the bond area of TAB. Disadvantages: 1. COG can only be used at a certain resolution level where the lines are not too fine. At very fine pitches COG becomes difficult to test, and TAB is the preferred approach. 2. It may be more cost-effective to use TAB or COB, if a designer has to integrate a keypad or indicator around the display. 3. The active area is not centered within the outline but offset, because of the area where the circuits are. Since the Chip-On-Glass integrated circuit has been invented by Epson, COG technology became very popular due to the demand for more compact applications. In the near future we will see this IC mounting method finding its applications in many other equipment than cellular phones, PDA's, computer network servers, satellite receivers, etc. This year Tianma Microelectronics is going to announce 7 standard Chip-On-Glass LCD modules available for the regular product lead time. TAPE AUTOMATED BONDING (TAB) TAPE CARRIER PACKAGE Tape Automated Bonding (TAB) LCD driver or controller electronics are encapsulated in a thin, hard bubble package, of which the drive leads extend from the bubble package on a thin plastic substrate. The adhesive along the edges is used to attach the TAB to the LCD glass and/or PCB. Tape Automated Bonding IC mounting method uses the same type of integrated circuits as Chip-On-Glass technology - Gold Bumped Flip Chips. After this type IC chip has been produced, we a gold bump is placed on the IC chip and then sealed onto the polymide board. (This procedure is called ILB or Inner Lead Bonding) and is how the TCP IC is produced. TAB LCD modules are always custom made from Tianma. Advantages: • Offers compactness (IC and its interfacing circuitry can be bent behind the LCD glass panel). • Some times more cost-effective than Chip-On-Glass, if a designer has to integrate a keypad or indicator around the display. • The active area is centered (differently from COG). • Can provide interfacing at very fine pitches. Disadvantages: • The bonding area is weak. Less reliable than COG. • More expensive than COG. Even though TAB LCD modules use the same type of IC as COG, tape automated bonding requires a package. TYPES OF LCD BACK LIGHT LED (Light-Emitting Diode) - Consists of surface mount LED’s, which are situated in series along the bottom of a shallow plastic tray. Features: •Available Colors: Yellow-Green (standard), Red, Amber, Green, Blue, White •Life time: long, typically 50,000 hours •Operating temperature range: -30 to +70 degrees C •Requires low voltage DC. No DC/AC inverter required •Simple connection +5 VDC (Anode) and ground (Cathode) •Two methods: matrix (array)or edge lighting •The typical voltage for all standard LED versions of LCE modules is 4.2 VDC. EL ( Electro Luminescent) - A thin membrane consisting of two coated electrode plates with an aluminum reflector. When AC voltage is applied to the electrodes, the electrons collide with the light emission core. The energy given off is light. Inverter (DC to AC) is used to power electro luminescent lamps. Features: •Available Colors: White (standard), Blue, Yellow-Green •Service Life: 4000 hours (driven with inverter, 20 C temp, and 70% humidity) and 1500 hours (driven with a fixed power supply and frequency generator, 20 C temp, and 70% humidity) •Operating temperature range: -20 to +50 degrees C CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp) - A miniature high voltage cold cathode (field emission) lamp made of lead-glass with mercury inside that provides fluorescent back lighting or edge lighting . Uses a diffusing light guide. High brightness, high efficiency and vibration-proof. Features: •Available Colors: White (standard) •Life time: 15,000; 20,000 hours •Operating temperature range: -20 to +50 degrees C •Low power consumption and excellent lighting characteristics •Easy intensity control •Low heat generation and thin diameter lamps FIBER OPTIC - Fiber optics are flattened and then sandwiched between two pieces of pliable plastic. The top piece is used as the diffuser. The opposite ends are tied into a coupler, which is connected to an LED or Halogen light source. Features: •Available Colors: White, Green, Blue, Amber and Red •Life time: long, remote light source offers 10,000 to 100,000 hours life and easy replacement. •Operating temperature range (optical fibers): -40 to +85 degrees C •Low power consumption. Sources require less power than EL, CCFL, or LED Array and no inverter. As low as 10-20mA at 2vdc •Compact, panels are thin and sources are smaller than EL or CCFL inverters •Heat free, adds no heat or EMI to interfere with switch operation •Very durable. Optical Fibers are not affected by extremes in humidity (0% to 100%) and temperature TYPES OF CONNECTORS FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) - cable with two smooth or corrugated, but essentially flat, surfaces. Attached to the PCB by soldering or plugging into a zero insertion force connector. Very reliable. FPC (Flexible Print Circuit) is a circuit substrate of patterning Cu electrode with Polyimide film as a base. Usually offers more flexibility than Flexible Flat Cables. Heat Seal - consists of microscopic metal particles within the Hot Melt Adhesive covering the entire area. Very flexible and eligible for connecting a large number of terminals simultaneously by single sealing operation. Pins - allow self-aligning connection to printed circuit boards via plug in strip sockets. Work well in harsh environments. Two conventional methods: DIL (Dual-In-Line) and SIL (SingleIn-Line). Zebra Strips or “Elastomeric” - strips of silicone rubber made up of sequentially spaced conductive and non-conductive material. This is the most common connection method for complete LCD modules. Resistant to shock and vibration. TEMPERATURE CHARACTERISTICS TN MODULES OPERATING STN MODULES STORAGE NORMAL RANGE WIDE 0 ~ +50 -20 ~ +70 -20 ~ +60 RANGE -30 ~ +80 -20 ~ +60 RANGE -20 ~ +70 -30 ~ +80 STN PANELS OPERATING STORAGE 0 ~ +50 -20 ~ +60 -10 ~ +60 -20 ~ +70 WIDE RANGE 0 ~ +50 WIDE TN PANELS RANGE STORAGE NORMAL RANGE NORMAL OPERATING -20 ~ +70 -30 ~ +80 -30 ~ +80 -40 ~ +90 OPERATING STORAGE RANGE 0 ~ +50 -20 ~ +60 WIDE -20 ~ +70 -30 ~ +80 -30 ~ +85 -40 ~ +90 NORMAL RANGE The above numbers are in °C.