* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II, Part 6: Ending the War in the Pacific and Aftermath
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
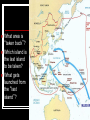
World War II, Part 6: Ending the War in the Pacific and Aftermath Goal 10 Essential Idea WWII ended with the dropping of two atomic bombs on Japan. Admiral Nimitz 1. Chester Nimitz – commander of the U.S. Navy in the Pacific Theater Japan Attacks the Philippines 2. Fighting in the Philippines: After attacking Pearl Harbor, the Japanese attacked military bases in the Philippines Troops there were led by General Douglas MacArthur MacArthur Ordered to Leave Americans were overwhelmed and driven to the Bataan Peninsula, where they ran out of supplies FDR ordered MacArthur to leave his troops behind so he would not be captured Bataan Death March Bataan Death March – 78,000 captured American troops were marched 65 miles to a prison camp, many dying along the way 3. The Doolittle Raids Aircraft carriers could not get close enough to Japan to send warplanes Airplanes did not have enough fuel to bomb Japan AND return Doolittle Raids – bombers flew over Japan, dropped bombs, and landed in China 4. Battle of the Coral Sea America and Australia were allies and America was sending Australia war supplies Japan sent warships to New Guinea to block the supply lines Battle of the Coral Sea Japan thought their operations were secret, but America had broken the Japanese navy’s code Admiral Nimitz sent two aircraft carriers to New Guinea to attack the Japanese navy Battle of the Coral Sea The two carriers took heavy damage (one sunk), but kept Japan off of New Guinea, keeping the supply line open 5. The Turning Point in the War in the Pacific Battle of Midway Japan wanted to lure American ships that were damaged by Pearl Harbor to Midway Island and destroy them Battle of Midway However, the Japanese code had been intercepted and broken again Nimitz ordered ships to Midway and set up an ambush Turning Point The Japanese navy lost 38 airplanes, 4 aircraft carriers, and 3,057 troops 6. Roosevelt Dies In April of 1945, FDR died of a stroke Harry S Truman became president and was now responsible for ending the war in the Pacific Strategy in the Pacific 7. Island Hopping American airplanes did not have enough fuel to fly all the way to Japan and back Island-Hopping – capture small islands in the Pacific Ocean and “hop” closer to Japan Once an island was captured, an airfield was built on it What area is “taken back”? Which island is the last island to be taken? What gets launched from the “last island”? 1. MacArthur Returns Battle of Leyte Gulf – the largest naval battle in history The Japanese used kamikaze attacks, where pilots intentionally crashed into American ships Kamikaze Attacks Americans suffered heavy damages, but were able to regain control of the Philippines 2. Iwo Jima 60,000 Marines “hopped” to the island of Iwo Jima Iwo Jima Marines used flame throwers and explosives to take the heavily fortified island Firebombing Tokyo American forces began firebombing Tokyo (using napalm) from Iwo Jima 3. Okinawa America needed an island closer to Japan, so they “hopped” to Okinawa 100,000 civilians died, many choosing to commit suicide rather than be captured Okinawa showed how brutal fighting would be if America attempted to invade mainland Japan 4. The Manhattan Project Before World War II broke out, Albert Einstein wrote a letter to FDR, informing him that Germany was trying to develop the atomic bomb The Manhattan Project was a secret government program created to develop the atomic bomb FIRST Should the Bomb be Used? Following the chaos on Okinawa, Truman decided that using the atomic bomb instead of a ground invasion would save American lives Potsdam Ultimatum – Truman demanded unconditional surrender, but Japan refused Boom On August 6th, 1945, “Little Boy” dropped on Hiroshima, killing over 120,000 Japan still did not surrender, so on August 9th, “Fat Man” landed on Nagasaki, killing over 74,000 V-J Day V-J Day – Japan surrendered to the United States, ending World War II Yalta Conference Meeting of the “Big Three” – FDR, Stalin, and Churchill They decided how to divide Germany after the war The United Nations Forms This was a new body of countries similar to the League of Nations 50 countries, including the United States, joined Nuremberg Trials These trials convicted and executed many former Nazi leaders The G.I. Bill Gave money to World War II veterans to build homes, start businesses, and go to college Why would such a bill be passed (think of World War I)? Economic Growth and the Growth of Suburbia Economic Growth: War production and the G.I. Bill helped the economy finally recover Growth of Suburbs – people began to move in to suburbs, which provided cheaper houses Levittown – the first suburb The Baby Boom A major rise in the birth rate that occurred after soldiers returned and having families became affordable