* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II Study Guide
Propaganda in Japan during the Second Sino-Japanese War and World War II wikipedia , lookup
Wang Jingwei regime wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American mutilation of Japanese war dead wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aleutian Islands Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Magic (cryptography) wikipedia , lookup
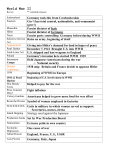
World War II Review Global War: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. George Marshall – US Army Chief of Staff/planner of the D-Day Invasion List the major Generals of the war – Patton, MacArthur, Marshall, Eisenhower, Kamikazes – Japanese suicide pilots Holocaust - attempted extermination of the Jews in Europe by the Nazi’s. Similarities between Italy, Germany, and Japan – attempted to solve problems through conquest of neighboring lands/sought empires, land and resources, and revenge American Policy during the early years of WWII – Isolationism/remain neutral while supplying weapons to GB/France Pearl Harbor attack – prompted the US to enter the war in December 1941/ Japanese then attacked Clark Air Field the American air base in the Philippines “Code Talkers” – Navajo radio operators/ helped secure communication in the pacific D-Day – allied forces landing on the Normandy Coast of France List the main battles of the Pacific – Guadalcanal, Coral Sea, Midway, Iwo Jima, Okinawa Hiroshima and Nagasaki – dropping the atomic bombs on these cities brought an end to WWII Nuremberg Trials – important idea was established that individuals are responsible for their own actions- can’t just follow orders The Battle of the Atlantic – Americans fought to keep German submarines from isolating Great Britain V-E Day – the end of the war in Europe May 8, 1945 “I shall return” – spoken by Douglas MacArthur in the Philippines Island Hopping – strategy used by American forces in the Pacific to get into position to bomb the Japanese Homeland Nuremberg Laws – passed in 1935 to strip the Jews of their citizenship Concentration camps – camps used by the Nazi’s to imprison/exterminated “undesirable” members of society Battle of the Bulge – Germans fought to save their homeland/December 1944 largest battle in Western Europe during WWII Battle of Stalingrad – most Nazi’s believed the war was lost at the end of this battle Battle of Midway – The allies sunk all four Japanese carriers and 250 planes/protected Hawaii/Japanese last offensive move of the war Manhattan Project – code name for the development of the atomic bomb War Refugee Board – created by FDR in 1944 to help the Jews/saved 200,000 War at Home: 24. Office of War Mobilization – the purpose was to centralize agencies dealing with the war 25. “cost-plus” system – Government sought to guarantee profits for businesses engaged in war production/cost of development plus a percentage 26. deficit spending –using borrowed money to finance war production 27. shortages of consumer items – prevented Americans from spending the high wartime wages/factories only making war goods 28. Office of War Information – main goal to boost morale and patriotism – posters & ads 29. Describe women workers - all ages, ethnic and economic backgrounds/became welders and steel workers 30. Compare women workers status compared with that of men – women were paid less for the same work due to lack of seniority 31. Describe racial conditions during the war – AA women filed law suits to be hired in industrial jobs/the war highlighted the injustices/racism in the north included discrimination in housing, employment, education – ended up in urban ghettos 32. causes for evacuation of Japanese to internment camps – prejudice inflamed by Pearl Harbor/protection of Japanese 33. What brought the US out of the Depression? Deficit spending and massive production of WWII 34. liberty Ships – huge ships = moving cities/mass produced/ invented by Henry Kaiser 35. popular culture included – pocket books, movies, baseball 36. goal of rationing – distribute scarce items fairly 37. goal of collection campaigns – keep people actively involved in the war effort 38. expectations for women after the war – they would leave jobs and return to homemaking, cooking, and childcare 39. “Double V” campaign – victory in war and racial equality at home 40. Victory gardens – produced 1/3 of all fruits and vegetables 41. A. Phillip Randolph – threatening a march on Washington to end discrimination in defense plants/civil rights worker Extra: 42. Robert Woodruff – entrepreneurs/pocket books/created new markets for products 43. Financing the war – deficit spending, war bonds, raised income taxes 44. Wannsee Conference – announced the total extermination of the all Jews as the solution to the Jewish problem 45. Shortages – caused by disruption of foreign trade due to German submarine 46. Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) – used sit-ins to promote racial equality 47. Poland – Hitler’s aggressive actions here trigger WWII 48. Stalin – urged allies to attack Western Europe but instead they attacked Italy leading to Cold War tensions World War II Open Response: Answer the question in PARAGRAPH form. Underline all key information in the questions and your answer. (50 points) President Truman considered the Atom bomb a military weapon and never had second thoughts regarding its use against the Japanese in World War II. A. What were some (4) of the alternatives to using the atomic bomb? B. Discuss the positive and negative outcomes for each of the four alternatives. C. Do you think any of these alternatives would have been better than the actions taken? Explain. 1. Allied planners had already worked out a plan for a massive invasion of Japan. 2. A naval blockade or continued conventional bombing could also defeat Japan. 3. Demonstrate new weapon on a deserted island to show Japanese its awesome power. 4. Soften insistence on unconditional surrender. The heavy American casualties at Iwo Jima and Okinawa were a factor in the committees’ unanimous support for using the bomb.