* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science (done) > Mrs Potts > 11A5 Physics
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Fuse (electrical) wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Overhead line wikipedia , lookup
Electrical connector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Industrial and multiphase power plugs and sockets wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring wikipedia , lookup
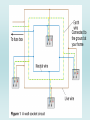
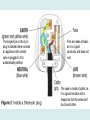
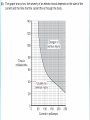
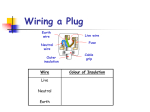
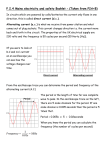
TITLE: Mains Electricity 2 Objectives – to know: • What is the casing of a mains socket or plug made form and why? – grade C • What is in a mains cable? – grade C • Why does a 3 pin plug include an earth pin? Outcomes: Complete worksheet on VLE KEY WORDS: Fuse current Circuit breaker mains Earthed Double Insulated Neutral Live earth • Most electrical appliances are connected to the mains using cable and a three-pin plug. • You must know: – The structure of electrical cables (twocore and three-core). – The structure and wiring of a three-pin plug. Connected to the ground at your home The longest pin on the 3 pin plug is attached here so when an appliance with a metal case is plugged in tit is automatically earthed. Pins are made of brass as it is a good conductor and does not rust. The case is made of plastic as it is a good insulator and is shaped so that the wires don’t touch each other. Why do some plugs only have two pins? Some sockets in Europe have two round slots for the pins. Does this mean that the appliances are not earthed? Instead of having a pin for the earth connection, the plug has a clip on the side. This clip corresponds to a contact point in the socket and connects the appliance to earth. This plug and socket system is sometimes referred to as “Continental European”. Identifying wrongly-wired plugs The Fuse A fuse is a thin piece of wire which will melt when too much current passes through it. Current is a flow of electrons (-) and is measured in amps (A). Example A 3A fuse will melt when the current is greater than 3A. When a fuse has ‘blown’, the wire inside it has melted. The Fuse When the wire melts, all current is stopped from reaching the appliance and switches it off. The fuse stops a large current from flowing through the appliance which could cause wires to overheat, melt or catch fire. The fuse rating is the maximum current that can pass through it. • The earth wire and fuse together protect the wiring of the circuit. • Candidates should have an understanding of the link between cable thickness and fuse value. • Cables of different thickness are used for different purposes. • The cables joining the wall sockets in a house must be much thicker than those then going from the walls to the light fittings. • The mains cables are thicker as more current passes along them than along a cable to a light fitting. • Due to resistance, if the wire is too thin, it will get very hot – if the wire gets dangerously hot a fire may result. The live wire carries a current that alternates between a negative and positive voltage. The neutral wire completes the circuit. It is kept at a zero voltage by the electricity company. The earth wire is a safety wire that is needed to earth appliances with a metal case. This makes it safer to touch the appliance if it develops a fault. What can go wrong! The most dangerous thing that can happen is that the live wire can become loose inside an appliance and touches the casing. This makes the casing LIVE! If you touch the LIVE casing, you could be electrocuted as you are providing a path for the electricity to flow. How does earthing work? • Appliances with metal cases are usually earthed. • Candidates should be aware that some appliances are double insulated, and therefore have no earth wire connection. What does ‘double insulated’ mean? Another way of improving the safety of electrical appliances is to make them double insulated. Double insulated appliances have plastic cases, without any wires connected to the case. This means that the case cannot become live, because plastic does not conduct electricity. So, if one layer of insulation is damaged the appliance is still safe for the user. symbol on double insulated appliance What is inside an electrical cable? A 3 core electrical cable contains three wires. copper These wires are made of copper because it is a good conductor of electricity. Each wire is made of thin strands of copper to keep the cable flexible. Each wire is encased in plastic to stop the wires touching and causing a short circuit. Plastic is used as it is a good insulator, as well as being tough and flexible. The whole cable is encased in another layer of plastic. insulating plastic 2 core and 3 core cables • Normally in appliances where there is no risk of an electric shock (ie double insulated) a two core cable is used. When it is plugged into an electrical outlet current flows into the appliance through one conductor and back into the outlet through the other. This completes the circuit and the appliance starts working. • In cases where there is a danger of an electric shock a 3 core cable should be used. The third conductor connects the metal part of the appliance to earth and any leakage that may occur due to a fault, will be safely conducted to ground. The copper braid acts as an earth wire • If an electrical fault causes too great a current, the circuit is disconnected by a fuse or a circuit breaker in the live wire. • When the current in a fuse wire exceeds the rating of the fuse it will melt, breaking the circuit. • Some circuits are protected by Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs). • RCCBs operate by detecting a difference in the current between the live and neutral wires. Knowledge of how the devices do this is not required. • Candidates should be aware of the fact that this device operates much faster than a fuse. • RCCB – detects difference between current in live and neutral (wires) • fuse – (overheats and) melts • The difference from the diagram is 100mA • The value for time for 100mA is 60 milliseconds in the usually no risk and very fast • Switches OFF at 60 milliseconds