* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The shoulder joint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
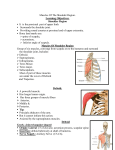
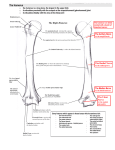
THE SHOULDER JOINT THE GLENOHUMERAL (GH) JOINT CLARIFICATION OF TERMS • Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle • Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115 OSTEOLOGY OF THE GH JOINT(BONES) • Scapula • • • • • • • Glenoid fossa Glenoid labrum Subscapular fossa Infraspinous fossa Supraspinous fossa Axillary border Acromion process (Axillary) (Vertebral) Scapula (Dorsal aspect) (Axillary) (Vertebral) OSTEOLOGY OF THE GH JOINT(BONES)…CONT • Humerus • • • • • • • • • Head Surgical neck Anatomical neck Shaft Greater tubercle Lesser tubercle Deltoid tuberosity Bicipital groove Bicipital ridges (Posterior aspect) Intertubercular groove (Bicepital groove) Intertubercular Groove (bicepital groove) Anatomical Neck Deltoid Tuberosity JOINT STRUCTURE OF THE GH JOINT • Ball and socket joint • Movement in all three planes (3 degrees of freedom) • Articulation between the humeral head of the humerus and the glenoid fossa of the scapula • One of the most movable joints in the body and, consequently, one the _______________ stable. Lippert, p131 JOINT MOVEMENT OF THE GH JOINT • Osteokinematics • • • • • • • • • • • Flexion Extension Hyperextension Abduction Adduction Medial rotation (internal rotation) Lateral rotation (external rotation) Horizontal abduction Horizontal adduction Circumduction Scaption JOINT MOVEMENT OF THE GH JOINT…CONT • Arthrokinematics • Concave-convex rule • The convex humeral head moves within the concave glenoid fossa • The convex joint surface (humeral head) moves in a direction opposite to the movement of the body segment (humeral shaft) • Flexion – humeral head glides _____________________ • Abduction – humeral head glides _____________________ • Extension – humeral head glides _____________________ • Adduction – humeral head glides _____________________ • Internal rotation – humeral head glides _____________________ • External rotation – humeral head glides _____________________ Lippert, p132 JOINT MOVEMENT OF THE GH JOINT…CONT • Arthrokinematics • The articular surface of the humeral head is greater than that of the glenoid fossa • If the humeral head simply rotated in the glenoid fossa, it would run out of articular surface before full abduction occurred • So, as abduction occurs, the humeral head rolls across the glenoid fossa and glides inferiorly (thanks to the rotator cuff) • Complete abduction can occur only with full external rotation SUPPORTING STRUCTURES OF THE GH JOINT • Rotator cuff • SITS muscles surround humeral head and actively hold it against the glenoid fossa • Capsular ligaments • Relatively loose capsule attaches the rim of the glenoid fossa and anatomic neck of the humerus • Coracohumeral ligaments • Connects coracoid process and anterior side of greater tubercle • Glenoid labrum • A fibrocartilaginous ring that encircles the rim of the glenoid fossa, deepening the socket and sealing the joint • Long head of the Biceps • The proximal portion of the tendon wraps around the superior aspect of the humeral head, providing anterior stability Mansfield, p58 MYOLOGY OF THE GH JOINT (MUSCLES) • • • • • • • • • • • Deltoid Pectoralis major Latissimus dorsi Teres major Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis Coracobrachialis Biceps brachii Triceps brachii, long head Deltoid: Anterior Origin Anterior surface of the lateral aspect of the clavicle Insertion Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus Action Sh flexion, HADD, Sh IR, Sh ABD Innervation Axillary n. Lippert, p136 Anterior Deltoid: Middle Origin Superior lateral surface of the acromion Insertion Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus Action Sh ABD, Sh flexion Innervation Axillary n. Middle Deltoid Lippert, p136 Deltoid: Posterior Origin Spine of the scapula Insertion Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus Action Sh extension, HABD, Sh ER Innervation Axillary n. Lippert, p136 Pectoralis Major Origin Clavicular portion: anterior margin of the medial portion of the clavicle Sternal portion: lateral margin of the manubrium and body of the sternum and cartilage of the first 6-7 ribs Insertion Crest of the greater tubercle of the humerus Action Clavicular: Sh IR, Sh flexion, HADD Sternal: Sh IR, Sh ADD, Sh extension, Sh depression Innervation Clavicular: lateral pectoral n. Sternal: lat & medial pectoral n. Mansfield, p82 Latissimus Dorsi Origin Thoracolumbar fascia, spinous processes of lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, posterior iliac crest, lower 4 ribs and inferior angle of scapula Insertion Floor of intertubercular groove of humerus Action Sh ADD, Sh extension, Sh IR, scapular depression Innervation Thoracodorsal n. “tidbit” Necessary for “crutchwalking” and transfers! Lippert, p137 Teres Major Origin Inferior angle of the scapula Insertion Crest of the lesser tubercle of the humerus Action Sh ADD, Sh extension, Sh IR Innervation Lower scapular n. Lippert, p138 SITS • Supraspinatus • Infraspinatus • Teres Minor • Subscapularis Supraspinatus Origin Supraspinatus fossa of the scapula Insertion Greater tubercle of the humerus Action Sh ABD, stabilization of the GH, slight ER Innervation Suprascapular n. “Tidbit” One of the rotator cuff muscles Lippert, p138 Infraspinatus Origin Infraspinatus fossa of the scapula Insertion Greater tubercle of the humerus Action Sh ER, stabilization of the GH joint Innervation Suprascapular n. “tidbit” One of the rotator cuff muscles Lippert, p138 Teres Minor Origin Posterior lateral border of the scapula near the inferior angle Insertion Greater tubercle of the humerus (inferior to the infraspinaus) Action Sh ER, stabilization of the GH joint Innervation Axillary n. Lippert, p139 Subscapularis Origin Subscapular fossa of the scapula Insertion Lesser tubercle of the humerus Action Sh IR, stabilization of the GH joint Innervation Upper and lower subscapular n. “tidbit” One of the rotator cuff muscles Lippert, p140 Coracobrachialis Origin Coracoid process of the scapula Insertion Medial aspect of the proximal shaft of the humerus Action Sh flexion Innervation Musculocutaneous n. Lippert, p140 Biceps Brachii Origin Long head: supraglenoid tubercle of glenoid fossa Short head: coracoid process of the scapula Insertion Radial tuberosity of the radius Action Sh flexion, elbow flexion, forearm supination Innervation Musculocutaneous n. “tidbit” The actions of the biceps brachii are “perfect” in combination for opening a bottle of wine. “The Corkscrew effect” Mansfield, p78 Biceps Brachii Long Head of the Triceps Brachii Origin Infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula Insertion Olecranon process of the ulna Action Sh extension, elbow extension Innervation Radial n. Mansfield, p80 MYOLOGY OF THE GH JOINT (MUSCLES)…CONT • Anatomical Relationsips • Muscles that stabilize are deep to muscles that move. • Therefore, glenohumeral joint muscles are superficial to shoulder girdle muscles • Deltoid: forms a superficial cap over the anterior, lateral and posterior sides of the shoulder • Anteriorly, pectoralis major covers most of the superficial chest wall • Biceps brachii and triceps brachii encompass most of the anterior and posterior arm, respectively • If the trapezius were removed, you would see the supraspinatus above the scapular spine and in descending order, the infraspinatus, teres minor and teres major below the scapular spine • The latissimus dorsi covers the lumbar and lower thoracic region of the back Lippert, p140 MYOLOGY OF THE GH JOINT (MUSCLES)…CONT • Anatomical Relationsips Lippert, p140 MYOLOGY OF THE GH JOINT (MUSCLES)…CONT • Summary of Muscle Action: (Lippert, p142) Action Muscles Flexion Anterior deltoid, pectoralis major (clavicular) Extension Posterior deltoid, lattisimus dorsi, teres major, pectoralis major (sternal) Hyperextension Latissimus dorsi, posterior deltoid Abduction Deltoid, supraspinatus Adduction Pectoralis major, teres major, latissimus dorsi Horizontal abduction Posterior deltoid, infraspinatus, teres minor Horizontal adduction Pectoralis major, anterior deltoid Lateral rotation Infraspinatus, teres minor, posterior deltoid Medial rotation Latissimus dorsi, teres major, subscapularis, pectoralis major, anterior deltoid MYOLOGY OF THE GH JOINT (MUSCLES)…CONT Lippert, p143 • Summary of Muscle Innervation: Muscle Nerve Segment Subscapularis Upper and lower subscapular C5, C6 Teres major Lower subscapular C5, C6 Pectoralis major Lateral and medial pectoral C5, C6, C7 & C8, T1 Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal C6, C7, C8 Supraspinatus Suprascapular C5, C6 Infraspinatus Suprascapular C5, C6 Deltoid Axillary C5, C6 Teres minor Axillary C5, C6 Coracobrachialis Musculocutaneous C6, C7 Biceps Musculocutaneous C5, C6 triceps radial C7, C8 What upper extremity muscles can you identify on him? REFERENCES • Lippert, L.S. (2011). Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy, 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis. • Mansfield, P.J., & Neumann, D.A. (2009). Essentials of Kinesiology for the Physical Therapist Assistant. St. Louis, MO: Mosby Elsevier.