* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Shoulder Anatomy PowerPoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
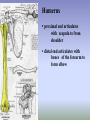
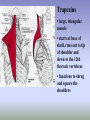
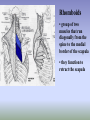
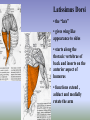
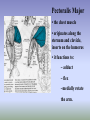
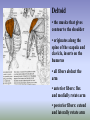
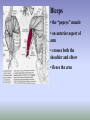
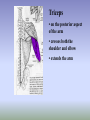
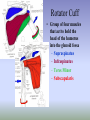
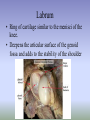
SHOULDER ANATOMY BONY ANATOMY Humerus • proximal end articulates with scapula to from shoulder • distal end articulates with bones of the forearm to form elbow Scapula • the shoulder blade Glenoid fossa has ring of cartilage called labrum to deepen the articular surface • the glenoid fossa of the scapula articulates with the humerus to form the glenohumeral joint (shoulder) • the acromion process articulates with the clavicle to from the acromioclavicular joint (tip of the shoulder) Clavicle • distally articulates with the acromion process to form the AC joint • Proximally articulates with the sternum to form SC joint Review of Joints • Glenoid fossa+humerus=glenohumeral joint (GH) (scapula) • Acromion process + clavicle =acromioclavicular (scapula) (AC) • Sternum + clavicle=sternoclavicular (SC) • Scapula+rib cage= scapulothoracic articulation MUSCLATURE Trapezius • large, triangular muscle • starts at base of skull, runs out to tip of shoulder and down to the 12th thoracic vertebrae • functions to shrug and square the shoulders Rhomboids • group of two muscles that run diagonally from the spine to the medial border of the scapula • they function to retract the scapula Latissimus Dorsi • the “lats” • gives wing like appearance to sides • starts along the thoracic vertebrae of back and inserts on the anterior aspect of humerus • functions extend , adduct and medially rotate the arm Pectoralis Major • the chest muscle • originates along the sternum and clavicle, inserts on the humerus • it functions to: ~ adduct ~ flex ~medially rotate the arm. Deltoid • the muslce that gives contour to the shoulder • originates along the spine of the scapula and clavicle, inserts on the humerus • all fibers abduct the arm • anterior fibers: flex and medially rotate arm • posterior fibers: extend and laterally rotate arm Biceps • the “popeye” muscle • on anterior aspect of arm • crosses both the shoulder and elbow • flexes the arm Triceps • on the posterior aspect of the arm • crosses both the shoulder and elbow • extends the arm Rotator Cuff • Group of four muscles that act to hold the head of the humerus into the glenoid fossa – Supraspinatus – Infraspinatus – Teres Minor – Subscapularis Rotator Cuff cont. • • • • Supraspinatus: 1st 10 degrees of abduction Infraspinatus: external rotation Teres minor: external rotation Subscapularis: internal rotation ** Note that there are no muscles on the inferior aspect of the shoulder!! This will be important when we talk about shoulder injuries Labrum • Ring of cartilage similar to the menisci of the knee. • Deepens the articular surface of the genoid fossa and adds to the stability of the shoulder