* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fruits and Seeds
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
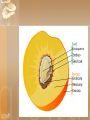
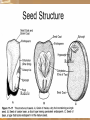
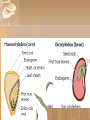
Fruits and Seeds introduction What is the result of the reproduction in flowers? What is it that flowers produce? Fruit and seeds. Both of these are the result of pollination, Pollination of Flowers Male- pollen- is transferred to the female’s stigma. A pollen tube grows down through the style into the ovary to deliver the sperm cell (pollen). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MQiszdkOwuU Fertilization occurs when the sperm and egg are joined= seed Fruit Fruits occur after a flower has been pollinated. The flower petals fall off The ovary and other surrounding parts enlarge and develop into a fruit https://www.youtube.com/watch?v =bwCpQflmQG4 The fruit is a seed bearing organ Encloses the seeds Protects the seed Means of dispersal of the seed Ripened, seed-bearing plant ovaries Vary in form, color, size, texture and number – aids in identification https://www.youtube.com/watch?v =4ttRgMj7PdQ 2 Types of Fruits Fleshy fruits Juicy and brightly colored Dry Fruits Dry fruits (nuts, beans) Generally grey, brown, or another dull color Thin and dry ovary wall Food is largely confined to the seeds. Seeds: A mature, fertilized ovules, or eggs, that are contained within a fruit. Range in sizes and shapes Disbursed in different manners: wind, animals, Radicle Radicle Radicle Seed Anatomy Embryo: a complete miniature plant in resting stage. It has roots, stems, and one or 2 leaves called cotyledons. Monocots Dicots have 1 cotyledon. have 2 cotyledons. EndospermFood Storage Tissue Tissues that contain stored, sugar, proteins and fats and oils. Used by the plant in its first stages of growth and development. Plants like corn have much of their food in the endosperm. Other plants like beans have theirs stored in the cotyledons Radicle Embryonic root First to emerge from seed coat during germination Seed Coverings Seed Coat Tissues that surrounds the embryo and endosperm Functions to protect the seed from moisture loss, injury, and other unfavorable conditions. Distribution of Seeds Wind Water Animals Explosive Some seeds have special adaptions to help them move farther from the parent plant ExplosivePea family As the pod dries in the sun tension is placed on the seed coat. When the seed coat burst it acts like a spring, ejecting the seed a distance from the parent Germination When the embryo begins to actively grow In order for seeds to germinate: Must be viable (good) Must not be dormant, or in a period where growth is not possible. Must be exposed to the right environment What is the right environment? Must have water (starts the germination process) Good temperatures Oxygen must be present Need either light or dark depending upon the type of seeds. 3 Stages in Germination Stage 1: Activation Inbibition (take up) of water This can happen if the seed is alive or dead Stage 2: Digestion Embryo begins to digest or eat the fats, proteins and sugars in the endosperm Stage 3: Seedling growth Cells at the growing points divide Cells elongate Radicle emerges: Radicle the growing point at the root (the first structure to emerge from the seed coat.