* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Reproduction
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
• Asexual reproduction is natural “cloning.”
Parts of the plant, such as leaves or
stems, produce roots and become an
independent plant.
Sexual Reproduction
• Sexual reproduction requires fusion of
male cells in the pollen grain with female
cells in the ovule.
Plant Life Cycle
Alternation of Generations
• Plants have a double life cycle with two
distinct forms:
• Sporophyte: diploid, produce haploid
spores by meiosis.
• Gametophyte: haploid, produce
gametes by mitosis.
Non-flowering plants
• Mosses, ferns, and related plants have
motile, swimming sperm.
• What kind of environmental conditions
would be required for reproduction in
these plants?
Moss Life Cycle
Fern Life Cycle
• Moss life cycle:
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o1z0
Vfo62Lg
• Fern life cycle:
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FhkY0duNjg
Conifers
• Conifers (also non-flowering plants) have
reduced gametophytes.
• Male gametophyte is contained in a dry
pollen grain.
• Female gametophyte is a few cells
inside of the structures that become
the seed.
Conifer life cycle
Conifer pollination
• Conifers are wind-pollinated plants.
• Chance allows some pollen to land on the
scales of female cones.
• Pollen germinates, grows a pollen tube
into the egg to allow sperm to fertilize the
egg.
• Life Cycle:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WPfRV8NWkk4
Plant Reproduction Song
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=35vPjd
TNRU0
Flowers
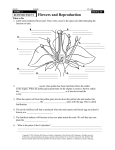
Flower Parts
Male Reproductive Structure
The stamen
consists of two
parts: Anther and
Filament
The anther is where
meiosis occurs to
produce haploid
pollen
The filament is a
stalk that supports
the anther
Female Reproductive Structure
The pistil consists of
the stigma, style and
ovary
The sticky stigma
receives the pollen
from the anther
The pollen grows a
tube down through
the style
Meiosis occurs in the
ovary to produce
haploid ovules
Pollination
Wind, insects or
other animals
transfer pollen from
the anther of one
flower to the stigma
of another
Flowers vary
depending on
pollination
mechanism
Fertilization
{ After pollen lands on the stigma, a pollen
tube grows down through the style to
ovary
{ Generative cell creates the two sperm
nuclei
{ Double fertilization occurs:
{ one sperm fertilizes the egg
{
one sperm the two polar nuclei
together
Angiosperm Life Cycle
Gametogenesis: Male
Gametogenesis: Female
Double Fertilization
Result of Double Fertilization
{ The sperm nucleus and egg nucleus join
to form a 2n (diploid) embryo
{ The other sperm nucleus and the two
polar nuclei join to form a 3n (triploid)
endosperm. The endosperm is the food
supply for the embryo.
{ First link
Flower to Fruit
Seed and Fruit Development
{ After
fertilization, the
petals and
sepals fall off
flower
{ Ovary “ripens”
into a fruit
{ The ovule
develops into a
seed
Seed Dispersal Mechanisms
Wind Dispersal - Flight mechanisms,
like parachutes, wings, etc.
Ex. Dandelion, maples, birch
Animal Dispersal - Fleshy fruits which
animals eat, drop undigested seeds in
feces or burrs which stick to
animals’ coats
Gravity Dispersal Heavy nuts fall to
ground and roll
ex. acorns
Water Dispersal - Plants
near water create floating
fruits
ex. coconuts