* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Terrestrial biomes
Conservation movement wikipedia , lookup
Polar ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
Old-growth forest wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Tropical Africa wikipedia , lookup
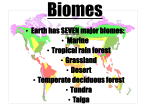
Terrestrial biomes biome • Definition- a major type of ecosystem with distinctive temperatures, precipitation, and organisms Major terrestrial biomes • • • • • • • Desert Tundra Deciduous forest Evergreen forest (taiga) Rainforest Steppe Prairie Desert biome • • • • Precipitation = 0 to 10 cm per year Most rain comes in a few thundershowers Lack of water makes desert cool at night 2 types of deserts – Cool (like deserts east of Rocky mtns.) – Hot (like deserts in Arizona and New Mexico Temperatures can go from 100 degrees F. to 40 degrees F. in same day Desert plants • • • • Store water in tissues Shallow, wide roots Many have spines The plant at right is the prickly pear cactus Old man cactus & aloe vera Desert animals • Get water from food • Some live underground • Some are nocturnal • Some have large ears to radiate heat • Animal at left is a fennec from Africa Thorny devil (Australia) & sidewinder (southwestern U.S.) Sahara desert Tundra biome • • • • Cold, windy & dry Fewest organisms of any other biome Short growing season (60 days) Permafrost – only top 8-10 cm of soil thaw in summer, area below stays frozen • Less than 25 cm of precipitation per year Tundra plants • Tundra plants are small, shallow-rooted, and grow close to ground • Willow trees grow only 1 meter tall from wind and limited space • Most are mosses, lichens, wildflowers, and grasses Tundra animals • Most have thick coats and wide feet • Migration – seasonal travel to find food • No reptiles or amphibians • Many migratory birds (few predators there) caribou Lemming evergreen forest (taiga) biome • Warm summers, long, cold winters • 40 to 200 cm precip. per yr. • Usually found on high mtns. of N. Amer., Europe, and Asia • Soil is poor because of slow decomposition of needles • Snow insulates soil from freezing Taiga plants • Trees have wax-covered needles to shed snow and hold moisture • Ferns and lichens grow in dim light on forest floor • Most taiga trees produce cones that contain seeds • Tree at left is a black spruce, often used as a Christmas tree Larch and jack pine (conifers) Taiga animals • Most adapted to cold & snow • Small rodents live under snow • Many large herbivores & predators moose lynx wolf Deciduous forest biome • • • • • Receives 50 to 300 cm precip. per yr. Temps. range from 30 deg.C to -30 deg.C Trees drop leaves in winter to conserve water 6 month growing season 3 layers: – Canopy (highest layer) – Understory (younger, smaller trees) – Floor (shrubs, ferns, mosses) Deciduous forest plants • Rich soil (humus) from falling leaves • Many are colorful in fall and winter • Tree on the right is a Japanese maple Red oak and sugar maple Deciduous forest animals • Diverse group of predators & herbivores • Adapted to cold • At right is a raccoon Pileated woodpecker and white-tailed deer Red fox and porcupine Rain forest biome • • • • • Average temp. is 25 deg. C year-round Precip ranges from 200 to 450 cm per yr. 12 month growing season Most diverse plants & animals of any biome Contain 70% of all terrestrial species but cover only 6% of earth’s surface • Canopy catches 99% of light hitting the forest • Soil is poor – warmth & moisture cause rapid decay of dead matter Rainforest plants • Shallow-rooted from poor soil • Some are epiphytes (live by hanging from trees) • Many exotic species of wood – teak, mahogany, balsa • Left is a mahogany guitar body Koli’I and orchid Rainforest animals • Adapted to different layers of forest • Some are arboreal (live entire life in trees) • Bird on right is bird-ofparadise Red-eyed frog & spider monkey Toucan & sloth Kinkajou & rainforest possum