* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biome: Deciduous Forest
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
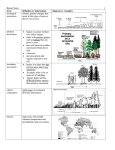
7-2 How Does Climate Affect the Nature and Locations of Biomes? Concept 7-2 Differences in average annual precipitation and temperature lead to the formation of tropical, temperate, and cold deserts, grasslands, and forests, and largely determine their locations. Climate Affects Where Organisms Can Live Biomes characterized by having similar: • Climate • Precipitation • Temperature • Soil • Plants • Animal Latitude and elevation Biomes are mosaics of patches Do not have distinct boundaries (ecotone) The Earth’s Major Biomes Generalized Effects of Elevation and Latitude on Climate and Biomes Natural Capital: Average Precipitation and Average Temperature as Limiting Factors Biome: Deciduous Forest Climate • Temperature: Temperate & Tropical • Precipitation: 75 – 250 cm per year Dominant Vegetation & Adaptations: • Hardwood (Deciduous) Trees • Loose leaves in winter to conserve energy Biome: Deciduous Forest Major Locations • North America, Europe, Australia, and Eastern Asia Characteristic Fauna • Black bear, white-tail deer, squirrels, raccoons, opossums Biome: Deciduous Forest Soil Characteristics • Very rich soil with high organic content Other Important Facts • Slow decomposition rates in the forest lead to high soil quality Temperate Rain Forest in Washington State, U.S. Climate Graphs of Tropical, Temperate, and Cold Forests Biome: Tropical Rainforest Climate • Temperature: Tropical • Precipitation: 200 – 400 cm per year Dominant Vegetation & Adaptations: • Broadleaf Evergreen trees • Large leaves to catch rare sunlight • Vines, epiphytes • Get moisture from the air, roots not in ground • All plants adapted to LOW light Biome: Tropical Rainforest Major Locations • South America, West Africa, Southeast Asia Characteristic Fauna • Monkeys, insects, amphibians, tropical birds Biome: Tropical Rainforest Soil Characteristics • POOR soil due to rapid rate of decomposition Other Important Facts • Stratification provides niches for specialized species – leads to high biodiversity Stratification of Specialized Plant and Animal Niches in a Tropical Rain Forest Biome: Grasslands Climate • Temperature: Tropical & Temperate • Precipitation: 10 – 60 cm per year Dominant Vegetation & Adaptations: • Sod-forming grasses which are adapted to fire • Grasses store most of their biomass in the roots, this ensures their recovery after a fire, and after grazers have eaten their tops Biome: Grasslands Major Locations • North American plains (prairies), Russia (steppes), South Africa (velds), Argentina (pampas), Africa (savanna) Characteristic Fauna • Grazers & Browsers Biome: Grasslands Soil Characteristics • Rich Soil • Has made the grasslands prime for human interference by agriculture Other Important Facts • Fire adapted • Large animals Climate Graphs of Tropical, Temperate, and Cold Grasslands Monoculture Crop Replacing Biologically Diverse Temperate Grassland Biome: Taiga (Boreal or Coniferous Forest) Climate • Temperature: Cold • Precipitation: 20- 60 cm (mostly in summer) Dominant Vegetation & Adaptations: • Coniferous evergreens • Small needle-shaped leaves with waxy coating to help conserve energy loss. Stay green all year because of relatively low solar intensity year-round Biome: Taiga (Boreal or Coniferous Forest) Major Locations • Northern North America (Canada), Northern Eurasia Characteristic Fauna • Bears, wolves, moose, lynx, and burrowing rodents Biome: Taiga (Boreal or Coniferous Forest) Soil Characteristics • Soil is thin and nutrient poor because of the acidic tannins in pine needles Other Important Facts • California’s Giant Redwoods (Sequoias) Biome: Tundra Climate • Temperature: Cold (grassland) • Precipitation: Less than 25 cm Dominant Vegetation & Adaptations: • Herbaceous plants • Low-growing plants, dwarf shrubs, lichens Biome: Tundra Major Locations • Northern latitudes of North America, Europe and northern Eurasia Characteristic Fauna • Caribou (reindeer), migratory waterfowl, arctic wolf, arctic fox, musk oxen, snowy owl Biome: Tundra Soil Characteristics • Permafrost!! • Very thin, fragile soil Other Important Facts • Most annual growth occurs in the 7-8 week long summer • Melting permafrost releases CH4 and CO2: both greenhouse gasses!! Biome: Chaparral (Scrub/Shrub Forest) Climate • Temperature: Temperate • Precipitation: 50 – 75 cm (mostly in winter) Dominant Vegetation & Adaptations: • Small trees with large hard leaves, spiny shrubs, adapted to fire • Burn easily • Seeds germinate when exposed to hot fire Biome: Chaparral (Scrub/Shrub Forest) Major Locations • Western North America, the Mediterranean Characteristic Fauna • Mule deer, chipmunks, jackrabbits, lizards, variety of birds Biome: Chaparral (Scrub/Shrub Forest) Soil Characteristics • Shallow and infertile soil Other Important Facts • Prone to fire in dry season • Desirable climate w/ risks! Chaparral Vegetation in Utah, U.S. Biome: Deserts (Hot & Cold) Climate • Temperature: Tropical, Temperate, Cold • Precipitation: Less than 25 cm Dominant Vegetation & Adaptations: • Cactus and other lowwater adapted plants (Succulents) Biome: Deserts (Hot & Cold) Major Locations • 30 North and South of the Equator Characteristic Fauna • Camels, reptiles, rodents (kangaroo rat – never drinks water) Biome: Deserts (Hot & Cold) Soil Characteristics • Coarse texture (sandy) • not good at holding moisture or nutrients Other Important Facts • Fragile ecosystem due to • • • • Slow plant growth Low species diversity Slow nutrient recycling Lack of water Climate Graphs of Three Types of Deserts La Mesa, CA Philadelphia Biome review! What are some of the traits that are similar between biomes of the same type? What is an ecotone? Which type of grassland is found in Africa? Which type of desert is found in Mongolia? Why is Antarctica not considered a part of a biome? Which biome do we live in? What is stratification? Where do we see it? If I hiked up a mountain, tell me what changes in vegetation I would experience. Why do pine trees have needle shaped leaves? Why do rainforest trees have broad-leaves? Why do deciduous trees lose their leaves? Explain how grasses are adapted to their environment.