* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Plantae
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
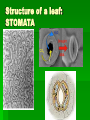
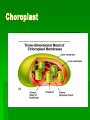
Kingdom Plantae Parts of a Plant- What do you remember from kindergarten? Seed Roots Stem Leaves Flower Seed Plants Characteristics Reproduction free from water Cones/Flowers Pollen Seeds Reproduction w/o Water Fertilization of gametes does not require water Allows seed plants to live almost anywhere Adaptations that allow repro w/o water include flowers or cones, pollination, and protection of embryos in seeds Cones/Flowers Gametophytes grow and mature in sporophytes Cones – gymnosperms Flowers – angiosperms Pollen Pollen grain – entire male gametophyte Sperm produced by pollen grain Carried to female reproductive structure by wind, water, insects, or small animals Transfer of pollen from male reproductive structure to female reproductive structure is called pollination Seeds Contain embryo of plant Have nutrients for the diploid embryo Have different adaptations for seed dispersal Some remain dormant waiting for ideal growing environments Angiosperms Group of flowering plants Monocots Dicots Monocot vs. Dicot Monocot Dicot Cotyledons (seed leaves) Leaf Veins Mono=1 Di=2 Parallel Branched Flower Parts (#petals, stamen, carpels, etc) Roots Always in multiples of 3 (ex. 3, 6, 9) In multiples of 4s and 5s fibrous Tap root Monocot or Dicot???? Monocot or Dicot? Monocots Vs. Dicots Texas A&M- Botany Flowers 1= petal 2= filament 3= anther (2+3=STAMEN) MALE 4= stigma 5=style 6=ovary (4+5+6=CARPEL) FEMALE 7=ovule Flower attaches to the stem Functions of parts Stamen- (anther + filament) These are the flower’s male parts. They have the pollen on them. Carpels-(stigma, style, ovary) female parts. Pollen travel down the style to the ovary where it fertilizes an egg to make a seed. Petals-Attract pollinators like bees and some birds Functions of Plant Parts Seed – this is what a new plant grows from in the presence of water. Growth stops= DORMANCY Roots – take in water from the soil Stem – transport of water from roots to leaves and flower Leaves – PHOTOSYNTHESIS Flower – Reproduction Ovary – develops into fruit in angiosperms Structure of a leaf STOMATA!!!!! Structure of a leaf: STOMATA Functions Leaves – photosynthesis, transpiration, and gas exchange Stomata – structure that allows gas exchange and transpiration Choroplast Characteristic of Kingdom Plantae All multicellular Eukaryotic cells Cell walls of cellulose Carry out photosynthesis Develop from multicellular embryos Turgor Pressure Results from osmotic pressure Main pressure of cell contents against cell wall Determined by water content of vacuoles Bryophytes Need water for reproduction Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts Lack vascular tissue to conduct water and nutrients Seedless Vascular Plants Ferns, club mosses, horsetails Need at least a thin layer of water for reproduction