* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Figure 38.2 Review of an idealized flower
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
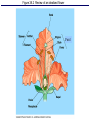
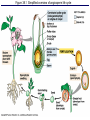
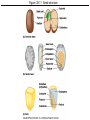
Figure 38.2 Review of an idealized flower Pistil Objective: You will be able to identify and give the function of the parts of a flower. Do Now: • Read pages 612 and 613 • For each part of the flower, write its function • This will take you a few minutes Male parts • Male part is called the stamen • The stamen consist of the anther and filament • Anther – Carries out meiosis to make pollen – Sperm cells are inside the pollen • Filament – Holds the anther into the air Female parts • Female part is called the pistil • The pistil is made of the stigma, style and ovary • Stigma is sticky to capture the pollen • Style is a passageway to the ovary • Ovary – Carries out meiosis to make eggs – The eggs are found within ovules Objective: You will be able to describe the events of pollination and fertilization. Do Now: • Read page 616 • What two things form from fertilization? Figure 38.5 Pollen grains have tough, ornate, and distinctive walls Pollination • Pollination is the transfer of the pollen from the anther to the stigma • If the pollen lands on a flower on the SAME plant it is called self-pollination – If it lands on a different individual then it is called cross-pollination • Pollinators are used to move the pollen Figure 38.3d1 Pollination modes Figure 38.1 Simplified overview of angiosperm life cycle Fertilization • Fertilization occurs within the ovule • There are actually two sperm cells • The first will fertilize the egg and form a zygote – This zygote will undergo cleavage to from an embryo Fertilization • The second sperm will fertilize a 2n cell and form a 3n cell called the endosperm – The endosperm is the food source for the embryo • This concept of two fertilizations is called double fertilization • It is unique to flowering plants. After Fertilization • The ovule itself will harden and become a seed • The ovary itself will change and become a fruit – The fruit is used for seed dispersal Figure 38.12 Development of a pea fruit (pod) Objective: You will be able to identify and describe the parts of a seed. Do Now: • Read page 618 • Give examples of fruits that everyone thinks are vegetables. Figure 38.11 Seed structure Seed Structure • The embryo consists of the hypocotyl and the epicotyl – Hypocotyl becomes the root – Epicotyl becomes the leaves and upper part of stem • Cotyledon is used as a food source • The seed coat protects the seed Seed germination • Once proper conditions are met, the seed will start to germinate. • Seed germination depends on water, oxygen and temperature • Why not light?