* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants-NOTES
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
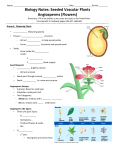
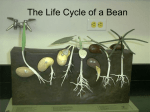
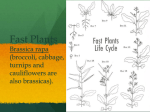
Plants! • Dominate _________________ • Extreme ____________________ • __________________ (<1mm in width to >100m in height) • >270,000________________ • Live a few weeks to over ________ years Did You Know? • Some plants produce seeds, others do not • Now Introducing…. The SEED Plants… SEED PLANTS… • 2 groups of seed plants are the _____________________ and ________________ Brassica rapa The plant that we will be working with in this unit is a _____________ ____________, and is known as the __________________________________. The scientific name for this plant is ____________________________ Gymnosperms! • Produce __________________ (not enclosed in _____________) and ____________________ • Most retain their leaves year-round • Most bear their seeds in cones SEED Plants also include… Angiosperms! (Flowering Plants) • Outnumber gymnosperms • One growing season includes germination, mature plant, and production of new seeds again = successful (10 years for gymnosperms) • Besides producing flowers, angiosperms produce _____________ (ripened __________) that protect and aid in dispersal of seeds • More diverse (What does diverse mean again? Oh yeah! VARIETY) Types of ROOTS • ___________: anchor the plant into the ground, receives water and nutrients for the plant from soil • ______________ (carrots): “taps into” the water supply that is in the ground • _____________________: numerous small roots that branch Root Hairs… Root hairs: extensions of roots that ____________ __________________ __________________ Hydroponics • Growing plants ____________ ________ by using solutions to provide the necessary _______________ for growth. Reaching into the SOIL… _________________- how the soil FEELS ________________- Chemicals needed for the functioning and growth of living things ______________-present in soil, is material that was once living and is important for fertile soil Soil may be considered ___________: mixture of 40% sand, 40% silt, 20% clay Fertilizer • Includes manure, ________________, _____________________, and ___________________ compounds, spread on or worked into soil to increase its capacity to support _______________ _______________. • ____________: Percentage of the 3 above chemicals found in purchased fertilizer. Root Adaptations • Roots are often adapted to store carbohydrates and water • Carbohydrates are converted to starch • (WE EAT THE STARCH!) STEMS: also known as pedicels or stalks of flowers • Varieties represent adaptations to the environment • STEMS: _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Animal • Also give support to leaves! protection Cactus Plant Potato Water storage and photosynthesis Storing energy as starch What are SEEDS? • Seeds contain __________________________________ • Good conditions trigger _______________ (evidence of growth from embryo to ________________) * ____________________________ * ____________________________ * ____________________________ 4 STAGES of PLANT Growth: • • • • _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ …..What are COTYLEDONS? Cotyledons • Seed leaves, it is where _____________ occurs and where ______ is stored for the seed. Monocots vs. Dicots • _____________ means one • ________ means two • Plants with one cotyledon are called __________________ • Plants with two cotyledons are called _______________. Leaves! • __________________________________ Now… • Onto the REPRODUCTIVE parts of PLANTS! • There are MALE and FEMALE parts! Parts of Flowers… • ___________: located at the base of a flower, protect the other parts of a developing flower before it opens, is often green • ___________: brightly-colored if part of an animal-pollinated plant, small or absent if part of a wind-pollinated plant Male Reproductive Parts of Flowers • ___________-male reproductive structure, consists of an _____________ and a _________________ • Anther-contains __________________ • ____________- stalk, supports an anther Female Reproductive Parts of Flowers • ______________- made up of the _________, __________, and _________ • Style- stalk-like, rises from the ovary, has a tip called the stigma that is sticky or has hairs to trap pollen grains, protects the pollen tube NOTE: • Most species of flowering plants have flowers with both stamens and pistils. They are called __________________. Some species have only stamens (male flowers) or only pistils (female flowers) ________________ • The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma to fertilize the egg (either occurring on the same plant or to another plant) • Self-pollination: Involves either the same flower, flowers on the same plant, or flowers from two genetically identical plants. • Cross Pollination: Involves two genetically different plants. Plants produced this way are called hybrids. Pollen Dispersal • Sea Grasses = by water • Oaks & grasses = by air (therefore, flowers are small and lack showy petals) • Many other species = by animals (showy flowers) • Successful Wind Pollination depends on: • Release of LARGE amounts of pollen • Ample circulation of air to carry pollen • Relative proximity of plants to one another • Dry weather Animal Pollinators (While obtaining nectar, desirable seeds, fruits) • • • • • • • • Bats Bees Beetles Moths Butterflies Hummingbirds Monkeys When animals are attracted to showy People flowers, they come to feed on the flower. Pollen sticks to their bodies and the animals deposit some of the pollen onto another flower that they go and feed on. Parts of a BEE BODY ____________________ • When pollen reaches the ovule Dispersal of Fruits and Seeds • Success of the seed plants comes from the development of fruits and seeds that are adapted for dispersing offspring. Fruits and seeds result from sexual reproduction in flowering plants. Fruits are adapted for dispersing seeds, and seeds function in the dispersal and propagation of plants. • Dispersal can be by animals, wind, water, forcible discharge, and gravity. Plant Responses • ________________: Response to gravity • ________________ Geotropism: Moving with gravity…roots growing DOWN (toward EARTH) • ________________ Geotropism: Stems, leaves, petals, reproductive parts growing UP (against gravity and away from Earth) Heliotropism • Response to _______________ _ • _________ = Plant reaching for the sunlight • ___________= plant droops Phototropism • Plants move in the direction of the _______________ ________________ Invasive Species • Any ______-____________ species (plant, animal, fungus, protist, bacteria) including its seeds, eggs, spores, or other biological material capable of propagating native species belonging to an ecosystem; and whose introduction does or is likely to cause economic or environmental harm or harm to human health. • Example: Buckthorn in Illinois Forest Preserves