* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction of Seed Plants - Science Class: Mrs. Boulougouras
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
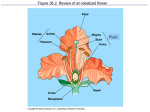
Reproduction of Seed Plants Chapter 24: Biology II Alternation of Generations • Diploid sporophyte generation alternates with a haploid gametophyte generation • Gametophyte plants produce male and female gametes: sperm and eggs • Gametes join zygote • Zygote begins the next sporophyte generation Life Cycle of Gymnosperms Life Cycle of Gymnosperms • Pollen cone: cone that produces male gametophytes in the form of pollen grains • Seed cone: cone that produces female gametophytes • Ovule: structure in seed cones in which female gametophytes develop Pollination • The gymnosperm life cycle typically takes 2 years to complete • Male cones release pollen grains and fertilizes some female cones • Pollen tube: structure grown by a pollen grain; contains two haploid sperm nuclei • Fertilization produces a diploid zygote; the new sporophyte plant • The zygote embryo develops in a seed Structure of Flowers • Reproductive organs composed of 4 kinds of specialized leaves: • Sepals • Petals • Stamens • Carpels Sepal • Outermost circle of flower parts that encloses a bud before it opens and protects the flower while it is developing Petal • Brightly-colored structure just inside the sepals; attracts insects and other pollinators to a flower Stamen • Male part of the flower • Anther – flower structure in which haploid male gametophytes are produced • Filament – a long, thin structure that supports and anther Carpel • Female part of the flower • Pistil – Several carpels fused together • Stigma – sticky portion at the top of the style where pollen grains frequently land • Style – supports the stigma • Ovary – a flower structure that contains one or more ovules from which female gametophytes are produced Perfect Flower • Male and female parts on the same flower Life Cycle of Angiosperms • Reproduction takes place within the flower • After pollination and fertilization, the seeds develop inside protective structures (fruit) • The mature sporophyte produces flowers • Each flower contains anthers and an ovary • 4 pollen grains are produced from the anther (male) Life Cycle of Angiosperms • The ovary contains ovules, in which the female gametophyte develops • Embryo sac: female gametophyte within the ovule of a flowering plant • If fertilized, a zygote will form and grow into a new sporophyte plant Pollination • Most angiosperms are pollinated by animals; i.e. insects, birds and bats • Flowers have bright colors, sweet nectars, etc. • Insect pollination increases chance that genes will be passed on Fertilization • A pollen grain lands on the stigma of an appropriate flower, producing a pollen tube • Endosperm: food-rich tissues that nourishes a seedling as it grows Fertilization • Double fertilization: fertilization in angiosperms, in which two distinct fertilization events take place between the male and female gametophytes Seed and Fruit Development • As seeds mature, the ovary walls thicken to form a fruit that encloses the developing seeds • Fruit: ripened ovary that contains angiosperm seeds Seed Dispersal • Animals • Wind • Water Seed Dormancy • Period of time during which a plant embryo is alive but not growing • Environmental factors such as temperature and moisture can cause a seed to end dormancy and germinate Seed Germination • Early growth stage of a plant embryo Vegetative Reproduction • Method of asexual reproduction used by many flowering plants • Naturally occurring in many plants • A technique used by many horticulturalists to produce many copies of an individual plant • Production of new plants from horizontal stems, plantlets and from underground roots Plant Propagation • Identical copies of a plant are made • Offspring produced from seedless plants – Cutting – Grafting: use of a stem as a scion – Budding: process of attaching a bud to a plant to produce a new branch Agriculture • Most of the people of the world depend on a few crop plants such as wheat, rice, and corn for the bulk of their food supply