* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
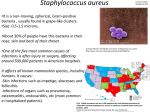
Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by Osmorhiza longistylis Root Extracts Jason N. Herold, Jennifer Antisdel, Bernadette Corbett, Del Stallwood Metropolitan Community College Omaha Nebraska Osmorhiza longistylis Smooth Sweet Cicely Anise-scented Habitat: moist woods Plant Height: 30-90 cm Flower Color: white Blooms: May-June Native Source: USDA Native American Uses Omaha Poultice of pounded root applied to boils. Winnebago Poultice of pounded root applied to wounds. Gilmore, M. R. 1919 Uses of Plants used by the Indians of the Missouri River Region. SI-BAE Annual Report #33 (p.107) Preparation of the Extracts Roots, stems and leaves separated Plant material washed with distilled water, then blotted dry Plant material ground in Waring Blender in 95% ethanol Plant material filtered off and discarded Ethanol distilled off, leaving an aqueous sample Preparation of Extracts Aqueous samples extracted with methylene chloride Dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate Liquid decanted into round bottomed flask Methylene chloride removed by distillation Diffusion Disk Method 24 hour cultures of S. aureus plated on brain heart agar 100 micrograms extract reconstituted in 20 microliters of DMSO and pipetted onto filter paper disks Disks placed on plates and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C Zones of inhibition measured and compared w/DMSO controls Results Root Extract Broth Dilution Method 24 hour Brain-Heart Broth cultures 100 micrograms of plant extract with 20 microliters DMSO incubated with 180 microliters of S. aureus culture for 2 and 24 hours at 37°C Incubation mixtures diluted 10,000-fold and 1,000,000-fold and spread plates prepared with 100 microliters of S. aureus Results Stem and leaf extracts did not inhibit growth when compared to DMSO control Root extracts inhibited growth by 12.2% and 25% when incubated for 2 and 24 hours, respectively Results Mean Inhibition Compared To DMSO Control 25 20 15 2 Hour % Inhibition 10 24 Hour 5 0 Root Stem Leaf Future Plans Dose-response curve of root extracts Fractionate root extract using HPLC and assay fractions for antibacterial activity Isolate and Identify active ingredient Acknowledgment Paul Evans collected the plants used in this study