* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
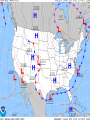
Download (a) high pressure, low pressure
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Convective storm detection wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Pangean megamonsoon wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
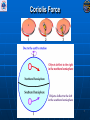
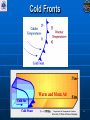
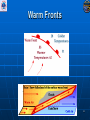
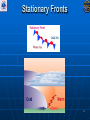
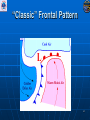
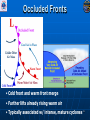
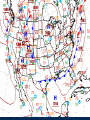
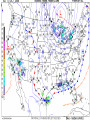
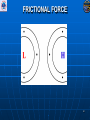
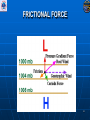
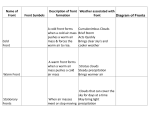
Air Masses, Clouds, and Fronts The “nuts and bolts” of day-to-day weather analysis and forecasting Frank Brody / Brian Hoeth National Weather Service Spaceflight Meteorology Group Johnson Space Center Houston, TX Weather and the Space Shuttle The Space Shuttle cannot fly: • Through thick low clouds • Through rain and snow • Near thunderstorms • Near lightning • In winds that are too strong • In strong turbulence 2 3 High and Low Pressure Isobars: Lines of constant pressure • aka “anticyclone” • Sinking air • Usually associated w/ fair weather • aka “cyclone” • Rising air • Usually associated w/ clouds4 and precipitation Forces and Winds Forces creating wind • Pressure Gradient Force • Coriolis Force • Frictional Force “Use the Force” 5 Pressure Gradient Force The pressure gradient force results in a net force that is directed from high pressure to low pressure 6 Coriolis Force 7 Geostrophic Wind • Wind blows parallel to isobars (lines of constant pressure) • Clockwise around High Pressure • Counterclockwise around Low Pressure 8 Frictional Force • Cause: Surface of earth is rough • Effect: Slows the wind down Coriolis force weakens, pressure gradient force becomes dominant • Result: Converging winds near lows and diverging winds near highs. 9 Cyclonic Circulation 10 Cold Fronts 11 Warm Fronts 12 Stationary Fronts 13 “Classic” Frontal Pattern 14 Occluded Fronts • Cold front and warm front merge • Further lifts already rising warm air • Typically associated w/ intense, mature cyclones 15 How to Read a Weather Map Temperature Pressure Weather Dew Point Wind 16 17 18 And now … It’s time for a pop quiz … A warm front exists when ___ air is rising over ___ air (a) cold, warm (b) hot, moist (c) warm, cold (d) cold, stable 20 A warm front exists when ___ air is rising over ___ air (a) cold, warm (b) hot, moist (c) warm, cold (d) cold, stable 21 At the surface, winds tend to flow ___ and ___ towards a center of a low pressure center (a) clockwise, outward (b) counterclockwise, outward (c) clockwise, inward (d) counterclockwise, inward 22 At the surface, winds tend to flow ___ and ___ towards a center of a low pressure center (a) clockwise, outward (b) counterclockwise, outward (c) clockwise, inward (d) counterclockwise, inward 23 The pressure gradient force results in a net force that is directed from ___ to ___ (a) high pressure, low pressure (b) low pressure, high pressure (c) left, right (d) right, left 24 The pressure gradient force results in a net force that is directed from ___ to ___ (a) high pressure, low pressure (b) low pressure, high pressure (c) left, right (d) right, left 25 Clouds How clouds are formed? Types of clouds • Cumulus • Stratus • Cirrus • Nimbus Clouds by height • High: Cirro • Mid: Alto • Low: Strato 26 Cloud Formation • Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint or when the air reaches saturation. • Air rises Lower pressure requires work Air is cooled! • Cooler air holds less water vapor some of the vapor condenses CLOUDS! 27 Cloud Types Latin Root Translation Example Cumulus Heap Fair weather cumulus Stratus Layer Altostratus Cirrus Curl of hair Cirrus Nimbus Rain Cumulonimbus 28 Clouds by Height Height in the atmosphere Prefix Cloud Base Height (ft) High Cirro Above 20,000 Mid Alto Between 6,000 and 20,000 Low Strato Below 6,000 29 Cirrus – “Curl of Hair” Thin, wispy clouds composed of ice crystals 30 Stratus ”Layer” Layered low clouds, sometimes patchy with poorly defined edges 31 Cirrostratus Cirro prefix: High Cloud Cirrus: “Curl of Hair” Thin, wispy clouds Stratus: “Layer” Poorly defined edges 32 “Halo around the sun” Cumulus – “Heap” Fair weather cumulus – small heaps of scattered clouds w/ flat bottoms and round tops Altocumulus – common 33 ahead of cold front Altocumulus Alto prefix: Mid Cloud Cumulus: “Heap” Flat bottoms, round tops 34 Stratocumulus Strato prefix: Low Cloud Cumulus: “Heap” Flat bottoms, round tops StratoCumulus – • Dark fluffy clouds • Relatively stable air • Not as menacing as it may appear 35 Nimbus – “Rain” Cumulonimbus Cumulo: “Heap” Nimbus: “Rain” Easier Translation: “Thunderstorm cloud” Nimbostratus - Widespread thick layer of cloud with poorly defined edges producing precipitation 36 Got any questions or have we left you in a fog??? Thank you for coming … buh bye now!! 37 Contact Info/Websites Frank Brody: [email protected] Brian Hoeth: [email protected] http://www.srh.noaa.gov/smg http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu http://virtualskies.arc.nasa.gov/main/mweather.html http://www.srh.weather.gov/jetstream/ http://www.windows.ucar.edu 38 Backup Slides 39 FRICTIONAL FORCE 40 FRICTIONAL FORCE 41