* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
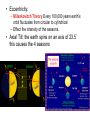
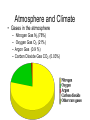
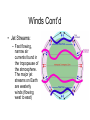
Climate Change Factors that Affect Climate • Atmosphere – The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity • Weather – the state of the atmosphere as measured on a scale of hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Day-today temperature and precipitation activity • Climate – the average atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. Sometimes referred to as the weather of the world. • Is climate change a new phenomena? – No, the earth’s climate conditions have changed over many years, as seen in soil samples and fossil records, however the human effect has added an amplification to the change of the climate. Earth and Sun • Solar Cycle: – Approx. every 11 years there is a change in solar radiation by about 0.1 % – Effect of climate: when the sun is stronger there is warmer climate trends • Movement of Earth in Space: – Involves tilt and wobble and creates seasons • Eccentricity: – Milankovitch Theory Every 100,000 years earth’s orbit fluctuates from circular to cylindrical – Effect the intensity of the seasons. • Axial Tilt: the earth spins on an axis of 23.5˚ this causes the 4 seasons Eccentricity QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. • Wobble:the earth wobbles every 433 days by about 20 feet at the poles. Minimum effect on climate although blamed for climate change. It is caused by ocean bottom pressures and atmospheric pressures. • Latitude: – the closer to the poles the less direct solar radiation there is. The sun’s rays hit an an angle – Effect the temperature Atmosphere and Climate • Gases in the atmosphere – – – – Nitrogen Gas N2 (78%) Oxygen Gas O2 (21%) Argon Gas (0.9 %) Carbon Dioxide Gas CO2 (0.03%) Winds • Winds and energy dispersion – The winds are created by differences in air temperature and they carry warm air to areas north and south of the equator • Winds and Ocean Currents – Winds at the surface of the ocean effect or push the water creating directions of ocean currents. • Winds and precipitation – The winds can carry moisture great distances from bodies of water allowing for tropical weather. It can also provide only dry air masses causing deserts. Winds Cont’d • Jet Streams: – Fast flowing, narrow air currents found in the tropopause of the atmosphere. The major jet streams on Earth are westerly winds (flowing west to east) Hydrosphere and Climate • Hydrosphere: – describes the combined mass of water found on, under, and over the surface of the planet. • Heat Capacity: defined as the heat required to raise unit mass of substance by one degree of temperature • Oceans and Lakes act as heat reservoirs – They hold onto the heat longer and keep moderate temperatures in comparison to the atmosphere above them. Water has a high heat capacity. • Albedo: a surfaces reflectivity of sun’s radiation. • Ice and snow reflect heat so help to cool the temperature of the Earth • Soil, trees and oceans have low albedo and absorb more heat helping to raise global temperatures. • Page 272 1-4, page 278 1-3 Unit 3, Chapter 7 Moving Continents and Climate Tectonic plates: move about 3 cm a year changing the shape of landmasses on earth. Effect ocean currents and heat distribution and also lead to more volcanic eruptions • Volcanic eruptions: – Release gases and particles that block out some radiation resulting in cooling of the atmosphere Human Activity and Climate • Anthropogenic: – Caused or produced by humans • Human technology and the atmosphere: – The industrial revolution has increase the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere along with other pollutants leading to global warming increases – Humans have also impacted the ozone layer by weakening it with CFC’s. This issues has started to repair itself now that CFC are banned.