* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ch. 8 population change
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
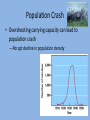
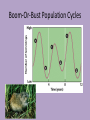
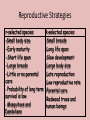
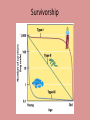
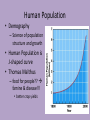
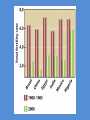
Chapter 8 Population Change Overview of Chapter 8 • • • • • Principles of Population Ecology Reproductive Strategies The Human Population Demographics of Countries Demographics of United States Principles of Population Ecology • Population Ecology – Study of populations and why their numbers change over time – Important for • Endangered species • Invasive species • Population – Group of individuals of same species living in the same geographic area at the same time Population Density • Population density – The number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume at a given time – Ex: minnows per Liter of pond water Change in Population Size Change in Population Size Calculating Population Change Growth rate Death rate Emigration rate r = (b – d) + (i – e) Birth rate Immigration rate CRUDE BIRTH/DEATH RATE are calculated per 1000 people Maximum Population Growth • Intrinsic Rate of Growth (Biotic Potential) – Growth rate under ideal conditions – J- Shaped Curve (exponential growth) Environmental Resistance • Environmental limits (resistance) – Prevent indefinite reproduction – Unfavorable food, water, shelter, predation, etc. • Carrying Capacity (K) – Maximum # of individuals an environment can support – Causes leveling off of exponential growth – S- shaped curve of logistic population growth Check for understanding • 4 - I can explain to my peers why populations cant grow in size forever. • 3 - I understand what limits populations from growing in size unstopped. • 2 - I understand carrying capacity, but need more practice. • 1 - huh? Exponential growth? Carrying capacity? Population Crash • Overshooting carrying capacity can lead to population crash – Abrupt decline in population density Factors That Affect Population Size • Density Dependent Factor – Factor whose effect on population changes as population density changes – Examples: • Predation • Disease • Competition – Sometimes cause Boom-or-Bust Population Cycles Boom-Or-Bust Population Cycles Case Study- Predator Prey Dynamics on Isle Royale • As wolf population increases, moose population decreases (and vice versa) Factors That Affect Population Size • Density Independent Factors – Factors that affects population size, but is not influenced by changes in population density – Examples: • Killing frost • Severe blizzard • Fire Check for understanding • 4 - I can explain to my peers different ways that populations increase in size and factors that limit uncontrollable population growth. • 3 - I understand different ways that populations grow and limitations to their growth. • 2 - I understand how exponential growth, boom and bust, and carrying capacity, but I need more practice. • 1 - I am lost population growth. Reproductive Strategies r-selected species k-selected species -Small body size -Small broods - Early maturity -Long life span - Short life span -Slow development - Large broods -Large body size - Little or no parental -Late reproduction care -Low reproductive rate - Probability of long term -Parental care survival is low -Redwood trees and - Mosquitoes and human beings Dandelions Survivorship Some populations fit two curves • Herring Gulls • Type III (young) & Type II Check for understanding • 4 - I can explain to my peers how reproductive strategies vary from survivorship types. • 3 - I understand how reproductive strategies vary from survivorship types . • 2 - I understand, I think, but need to review my notes on reproductive strategies and survivorship types. • 1 - Aren’t all organisms the same???? Human Population • Demography – Science of population structure and growth • Human Population is J-shaped curve • Thomas Malthus – food for people?? famine & disease!!! • better crop yields Human Population 1 Billion 1800 2 Billion 1930 3 Billion 1960 4 Billion 1975 5 Billion 1987 6 Billion 1999 6.6 Billion 2006 Population Increase in Mexico Projecting Future Populations • Population is increasing; why is death rate going down? • Growth rate (r) has started to decline • Zero-population growth: birth rate and death rate are equal (S – shaped curve) • Projections for 2050 – variation due to fertility rate of less developed countries – Low = 7.7 billion – High = 10.6 billion – Most likely = 9.1 billion Demographics of Countries • Highly developed countries – Ex: US, Japan, Germany – – low birth rates, low infant mortality rates (6% US; 54% world), long life expectancy (77 US, 67 world), high per-capita GNI PPP ($34,000, $7,000) • Developing countries: – moderately developed countries (Ex: Mexico, Thailand) – high infant mortality/birth rates, but declining – less developed countries (Bangladesh, Niger, Ethiopia) Growth rate • Doubling time!! – amount of time for an area to double = 70/r (r = growth rate as %) – Which type of country has shorter doubling time? • Replacement-level fertility – typically 2.1 children – Total fertility rate (world) is above replacement level (about 2.5) – Impacting factors: infant mortality rate, population momentum by ## of young females, need/lack of need for children to work (rural), education (especially of women!!) Check for understanding • 4 - I can explain to my peers zero population growth, total fertility rate, replacement level fertility, and doubling time. • 3 - I understand zero population growth, total fertility rate, replacement level fertility, and doubling time. • 2 - I understand, I think, but need to review my notes on zero population growth, total fertility rate, replacement level fertility, and doubling time • 1 - I understand some of the terms, but not all. Demographic Stages • Pre-industrial Stage – Birth and death rates high – poor medical care, limited food supply – Modest population growth • Transitional Stage – Lowered death rate – higher education/improved conditions – Rapid population growth • Industrial Stage – Birth rate decline – urbanization decreases economic reason for many kids, women educated/work, retirement safety nets reduce it – Population growth slow • Post Industrial Stage – Low birth and death rates – Population growth very slow Demographic Stages Age Structure • The number and proportion of people at each age in a population Demographics of Specific Countries World-wide • 29% of human population is under age 15 • Could cause large increase in birth rates Check for understanding • 4 - I can explain to my peers all the different demographic stages, why they occur AND how to read age structure graphs. I should just drop out of HS now . • 3 - I understand all the different demographic stages, why they occur AND how to read age structure graphs . • 2 - I understand demographic transition and age structure graphs, BUT….. • 1 - I am lost and need to hear it all again.