* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download week 1 - Cloudfront.net
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
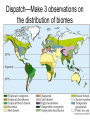
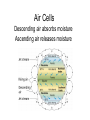
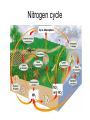
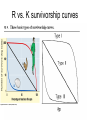
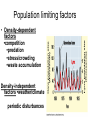
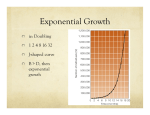
Week 1 • Ecology Chapters 52-54 Dispatch—Make 3 observations on the distribution of biomes Goal and Name same side • Line up for pic Air Cells Descending air absorbs moisture Ascending air releases moisture Group whiteboard • Draw a mountain • Predict what happens to air as it rises over a mountain How mountains affect rainfall. RAINSHADOW Show the O2 and CO2 cycle • Be as detailed as possible • One person will be picked to present Nitrogen cycle Dispatch • If your group needs to presentfind a group to listen and approve you • If your group is approved listen to group’s nitrogen presentation if they have all components, tell me Nitrogen Cycle Animation • http://www.dpi.vic.gov.au/dpi/vro/vrosite.ns f/pages/soilhealth_nitrogen-cycle Population vs. Community Population Ecology QUESTIONS: 1) What is a population? 2) What affects the size a population can get? Population • A population is a group of individuals of a single species that simultaneously occupy the same general area. • Two characteristics that affect populations are ________ and _______ Population characteristics Density~ # of individuals per unit of area • •counts •sample size estimate • •indirect indicators • •mark-recapture Dispersion~ pattern of spacing •random~ unpredictable, patternless spacing (a) •clumped~ patchy aggregation (b) •uniform~ even spacing (c) Density is the result of a dynamic interplay – Between processes that add individuals to a population and those that remove individuals from it Births and immigration add individuals to a population. Births Immigration PopuIation size Emigration Deaths Deaths and emigration remove individuals from a population. Activity: • Make a graph for a bacterial population and an elephant population Dispatch—Get a textbook 1) Draw an exponential growth curve? What species exhibit this growth? 2) What about the environment would make an r species exhibit exponential growth? 3) Describe what a population’s carry capacity is and what it means to the population? 4) Compare and contrast density- dependent to density-independent factors? Take our calendar and tell your tablemates 3 upcoming deadlines Pick up a growth half sheet and a paper that says class set Wilderness Park 9:30 TOMORROW Population Growth Models • Exponential model (blue) • idealized population in an unlimited environment (J-curve); r-selected species (r=per capita growth rate) • Logistic model (red) •carrying capacity (K): maximum population size that a particular environment can support (S-curve); Kselected species Demography: factors that affect growth & decline of populations • • • • Birthrate (natality, fecundity)~ # of offspring produced Death rate (mortality) Age structure~ relative number of individuals of each age Survivorship curve~ plot of numbers still alive at each age R vs. K survivorship curves Population life history “strategies” • r-selected (opportunistic) • K-selected (equilibrial) • • • • • Short maturation & lifespan Many (small) offspring; usually 1 (early) reproduction; no parental care High death rate • Ex:________ • Long maturation & lifespan Few (large) offspring; usually several (late) reproductions; extensive parental care Low death rate • Ex:____________ Population limiting factors • Density-dependent factors •competition •predation •stress/crowding •waste accumulation Density-independent factors •weather/climate periodic disturbances Community Ecology QUESTIONS: 1) What is a community? 2) Who are the members of this community? 3) What is a food chain? Differences in Community structure Community~ an assemblage of populations living close enough together for potential interaction. Many different ______. • Communities differ dramatically in their species richness (number of species) & relative abundance of different species How can we account for the species found together as members of a community? 2 Hypotheses: •Individualistic~ all the species just happened to live in the same area b/c they all had similar abiotic requirements. Example they all needed same temperature, rainfall, soil type which is why they live in the same habitat. •Interactive~ all the species are locked into association by mandatory biotic interactions. Species are found together b/c they have formed relationships +, - and o. Between Species TASK: Add a column to the right and give an example of each type of interaction Activity: Interaction Charades • I will give your group an interaction and you act it out