* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Humans in the Biosphere Powerpoint
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Animal genetic resources for food and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
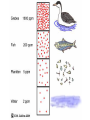
Humans in the Biosphere Ch. 6 Human Interaction There are four main activities by which humans affect the biosphere: – – – – Hunting and Gathering Agriculture Industry Urban Development What are some of the effects we see/experience as a result of these activities? Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources Renewable Resources – resources that can be replenished or regenerate in a relatively short amount of time – – Ex: trees, water, nutrients, etc. Although they are renewable, some of the are limited resources (not always readily available) Ex: Water can become a limited resource when there is a drought Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources Human activity can affect the quality and supply of renewable resources such as – – – – – Land Forests Fisheries Air Fresh Water Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources Nonrenewable Resources – resources that cannot be replenished by natural processes – – If they can be replenished, it takes millions and millions of years to replace it Ex: fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Biodiversity Biodiversity – the variety of organisms that are found on Earth Types of biodiversity – – – Ecosystem diversity Species diversity Genetic diversity Human activity can threaten and alter biodiversity Threats to Biodiversity Habitat alteration Demand for wildlife products Pollution – Biological magnification – concentrations of harmful substances increase in organisms higher in the food chain Introduced species – Invasive species – non-native species that rapidly reproduce and “choke out” native species Ex: kudzu Conserving Biodiversity Conservation efforts usually focus on protecting various: – Species/Populations – bald eagle, koala, etc. Ecosystems National Parks Wilderness Areas Nature/Wildlife Preserves