* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coastal sage scrub – note bare spots near shrubs Rabbit
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
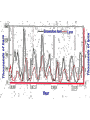
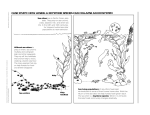
Competition Coastal sage scrub – note bare spots near shrubs Rabbit grazing – source of apparent competition Species Coexistence Serengeti National Park Species Coexistence Competition is a common feature of species interactions, yet often we find very similar species coexisting in nature, species that seem to need the same resources. How do they coexist? • Refuge from competition • Predation keeps populations of each species low enough that they do not compete • Resources may be variable in space and time, so that the species coexist because both do not find resource at same time Dung – a valuable, variable resource Dung Beetles Dung Fly Predation Great White Shark and Fur Seal Lions hunting – True Predator Moose Browsing – Partial Predator Parasitoid Wasp Specialists and Generalist Predators Advantages to being a specialist 1. Avoid interspecific competition 2. Allows evolution to overcome chemical defense 3. Allows evolution of cryptic coloration that matches prey - mostly for insects on plants 4. Increases chance of mate encounter Advantages of being a generalist 1. Flexibility in face of environmental uncertainty 2. Broad diet needed to get all necessary nutrients and vitamins 3. Avoid overdosing on any one toxin - mostly for animals grazing on chemically defended plants Pied Wagtail Caribou eating lichens Edible mussel – Mytilus edulis Black oystercatcher Bluegill sunfish Mink Muskrat Red grouse in heather Bank vole Tawny Owl Cinnabar Moth and Caterpillar on Ragwort Tansy Snowshoe hare and Lynx Lynx Ruffed Grouse Snowshoe hare Sea Otter Sea Urchin Kelp Forest Sea Otter eating Sea Urchin in Kelp Forest Comparison of kelp and urchin biomass with and without sea otters Kelp forest ecsystems with and without sea otters