* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Community Interactions - Welcome to the Home Page for
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
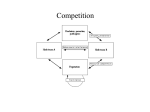
Community Interactions • Community – all the species in a given location at a given time • Habitat the physical environment they live in : Redwood forest • Niche – how a species uses the resources in its habitat – Builds nest in tree top vs. lower branches • Similar species coexist by Niche specialization. Paramecium caudatum Paramecium aurelia Competitive exclusion Competitive Exclusion • The more similar two species’ niches the more they compete. • No two species can share the exact same niche- one dies out. • Species evolve to diverge their niches by Resource Partitioning Competition for space on the rocks Weak competitors stuck higher up in the intertidal Resource Partitioning Bristly foxtail Indian mallow Smartweed Character Displacement Two species with same Beak size can not Coexist on same island One adaptive result of resource partitioning Types of Interspecific Interactions Species A Species B Commensalism + 0 Mutualism + + Competition - - Predation + - Parasitism + - Predator & Prey a Mutualism? Canadian lynx (dashed line) Snowshoe hares (solid line) Caulerpa taxifolia suffocating a marine ecosystem Do not post on Internet Number of species of ants Number of species of breeding birds Number of colonizing species of mosses and vascular plants recorded on Surtsey between 1965 and 1973 Mosses Vascular Plants Keystone species • Pisaster (Sea Star) defends tide pool from being taken over by mussels, barnacles. Sea Otters maintain Kelp forest • Otters are a Keystone species • Kelp are the base of the kelp forest community • Urchins eat kelp at their base • Otters eat urchins, keeping their numbers low. • Otter numbers along California are dropping. • Alaska- Orcas starting to eat otters, because seal numbers are dropping • No fish for seals Succession:Community Structure changes over time • Primary Succession: starts with no soil, just bare exposed rock – Progresses in stages until long term climax stage • Secondary Succession starts with the climax vegetation type – Disturbance (fire) resets timeline – Progresses in stages back to climax. 2-Barren Rock 1-Glacier Retreats 3-Moss and Lichen 4-Cottonwood and Alders 5-Spruce moves in 6-Spruce and Hemlock Climax Vegetation Fire Cycle in Chaparral Fire poppies in burn area Madrones sprouts from burl Ceanothus seedlings sprout after fire 1 month post fire Schmidts, M.J., D.A. Sims, J.A. Gamon California State University, Los Angeles, CA http://vcsars.calstatela.edu/eas_00/miriam/miriam_esa_00.html First spring 3 years post fire 20 and 40 years post fire Mosaic of ages burns